Industrial IoT - The Future of Manufacturing
Table of contents
- Industrial Revolution
- Smart Manufacturing
- Nine Pillars
- Reference Architectures
- Workloads
- IT Vs OT Security
- Readniess
Industrial Revolution
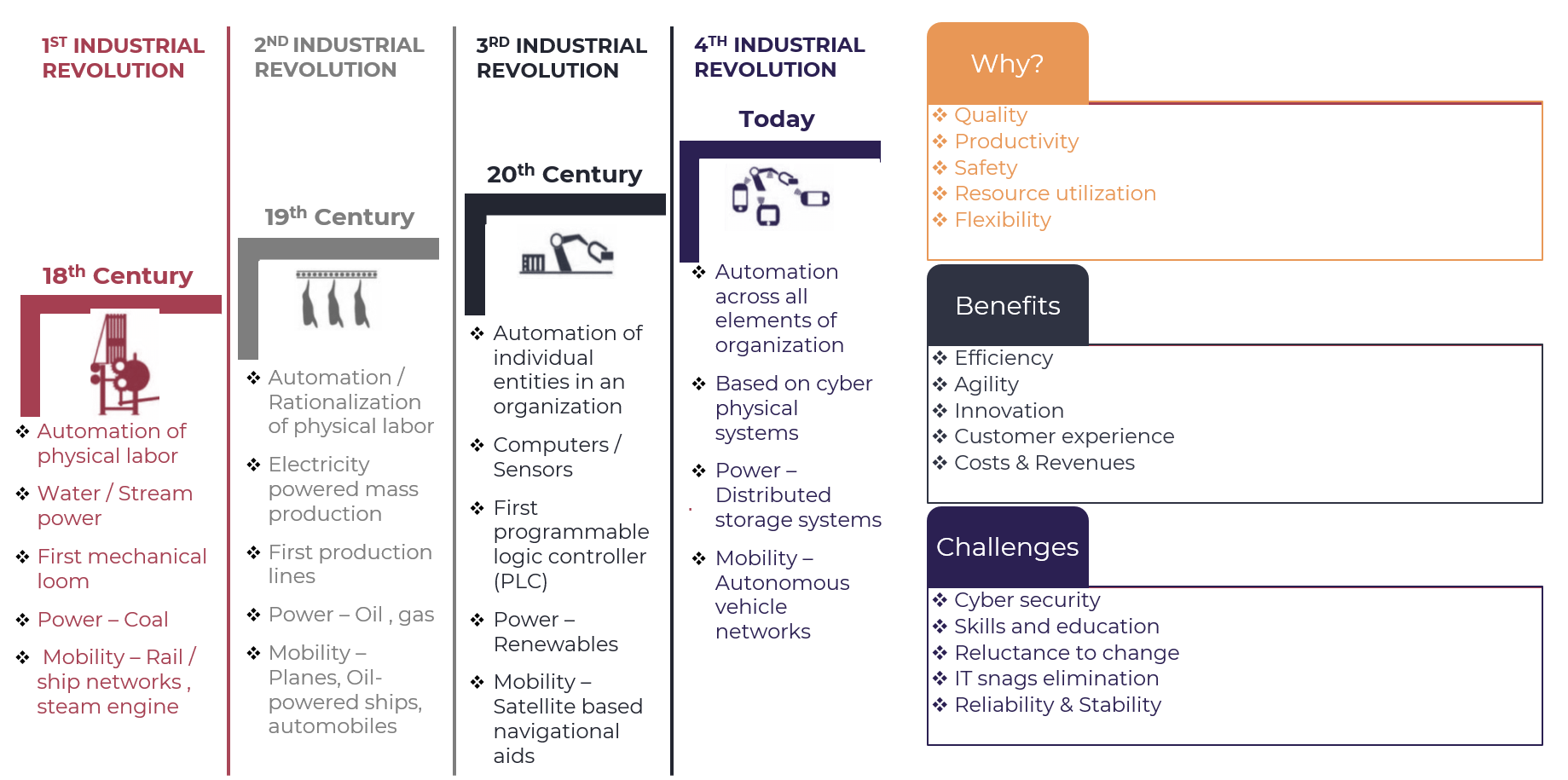 The Industrial Revolution was a pivotal period in human history, marking a significant shift from manual labor to machine-based manufacturing. This transformation had far-reaching consequences, impacting various aspects of society and shaping the modern world as we know it today.
The Industrial Revolution was a pivotal period in human history, marking a significant shift from manual labor to machine-based manufacturing. This transformation had far-reaching consequences, impacting various aspects of society and shaping the modern world as we know it today.
First Industrial Revolution (18th Century)
- Automation of Physical Labor
- Water/Stream Power
- The introduction of water-powered machinery marked a significant milestone in automation.
- First Mechanical Loom
- The invention of the mechanical loom revolutionized textile production, increasing efficiency and output
- Power - Coal
- Coal became a primary source of energy for industrial processes, driving growth and development.
- Mobility - Rail/Ship Networks, Steam Engine
- Advances in transportation enabled rapid movement of goods and people, further facilitating economic expansion.
- Water/Stream Power
Second Industrial Revolution (19th Century)
- Automation/Rationalization of Physical Labor
- Electricity-Powered Mass Production
- The widespread adoption of electricity transformed manufacturing processes, allowing for faster and more efficient production
- First Production Lines
- Assembly lines became a standard feature in factories, streamlining production and increasing productivity
- Power - Oil/Gas
- Fossil fuels emerged as a primary source of energy, fueling further industrialization.
- Mobility - Planes, Oil-Powered Ships, Automobiles
- Advances in transportation led to the development of new modes of travel, transforming global connectivity.
- Electricity-Powered Mass Production
Third Industrial Revolution (20th Century)
- Automation of Individual Entities in an Organization
- Computers/Sensors
- The rise of computers and sensors enabled automation within individual entities, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
- First Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
- The introduction of PLCs revolutionized industrial control systems, allowing for greater flexibility and adaptability.
- Power - Renewables
- Renewable energy sources began to gain prominence, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting sustainability.
- Mobility - Satellite-Based Navigational Aids
- Advances in satellite technology enabled precise navigation and communication, transforming industries such as aviation and maritime
- Computers/Sensors
Fourth Industrial Revolution
- Automation Across Entire Organizations
- Autonomy Across Entire Organizations
- The integration of artificial intelligence and robotics has led to increased autonomy across entire organizations.
- Based on Physical Systems
- Automation is now based on physical systems, leveraging the capabilities of sensors, actuators, and other devices.
- Powered by Distributed Storage
- Distributed storage solutions have enabled efficient management of data and resources, supporting widespread automation.
- Mobility - Autonomous Vehicles and Networks
- The development of autonomous vehicles and networks has transformed transportation systems, enhancing safety and efficiency.
- Autonomy Across Entire Organizations
Smart Manufacturing
Manufacturing Paradigms
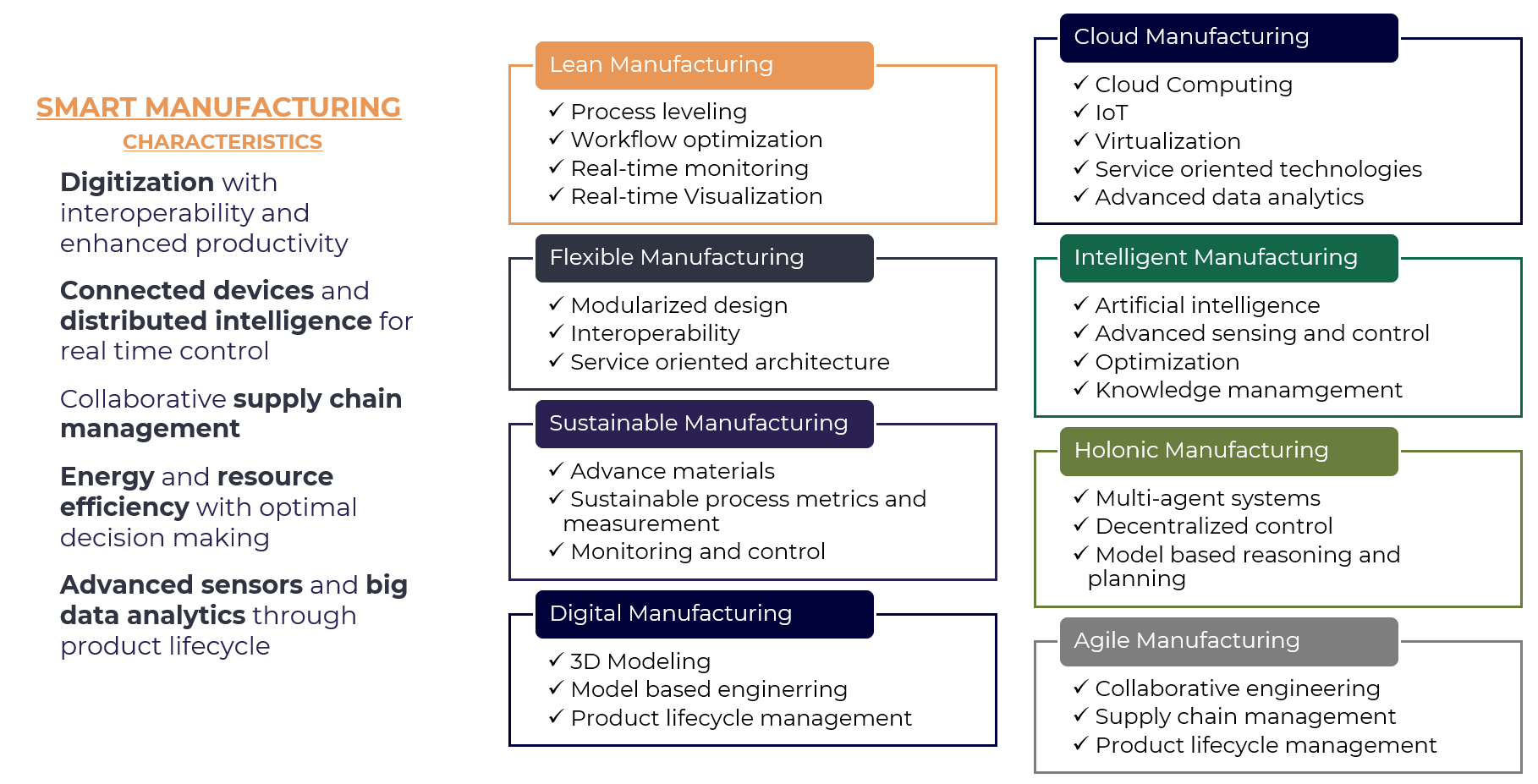 Smart manufacturing is an emerging trend that combines advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, IoT, and big data analytics to transform traditional manufacturing processes into more efficient, agile, and sustainable systems
Smart manufacturing is an emerging trend that combines advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, IoT, and big data analytics to transform traditional manufacturing processes into more efficient, agile, and sustainable systems
Characteristics of Smart Manufacturing:
- Digitization: The integration of digital technologies to create a virtual representation of the physical world.
- Connected Devices and Distributed Intelligence for Real-Time Control: The use of sensors, actuators, and control systems to monitor and control production processes in real-time.
- Collaborative Supply Chain Management: The integration of supply chain management with manufacturing to optimize inventory levels, reduce lead times, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Energy and Resource Efficiency through Optimal Decision-Making: The use of data analytics and machine learning algorithms to make informed decisions about energy consumption, resource allocation, and production planning.
- Advanced Sensors and Big Data Analytics Integrated into Product Lifecycle: The integration of sensors and big data analytics to monitor product performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize product design.
Manufacturing Paradigms:
- Lean Manufacturing: A paradigm that focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing value-added activities through continuous improvement and elimination of non-value-added tasks.
- Cloud Manufacturing: A paradigm that leverages cloud computing to enable flexible, scalable, and collaborative manufacturing processes.
- Intelligent Manufacturing: A paradigm that incorporates artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics to optimize production planning, quality control, and maintenance.
- Holonic Manufacturing: A paradigm that uses multi-agent systems, decentralized decision-making, and model-based reasoning to create self-organizing production systems.
- Agile Manufacturing: A paradigm that focuses on rapid response to changing market demands through flexible and adaptable manufacturing processes.
- Digital Manufacturing: A paradigm that leverages digital technologies such as 3D printing, simulation, and virtual reality to design, test, and manufacture products virtually.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: A paradigm that prioritizes environmental sustainability by reducing waste, conserving resources, and promoting eco-friendly practices throughout the product lifecycle.
- Flexible Manufacturing: A paradigm that enables rapid changeover between different production runs through modularized designs, interoperability, and real-time visualization.
- Intelligent Manufacturing: A paradigm that incorporates artificial intelligence, advanced sensing, control systems, optimization techniques, and knowledge management to optimize production processes.
Benefits of Smart Manufacturing:
- Increased Efficiency: Smart manufacturing enables automation, streamlines processes, and reduces labor costs.
- Improved Product Quality: Advanced sensors and analytics ensure consistent product quality, reducing defects and rework.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Smart manufacturing allows for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and personalized products tailored to customer needs.
- Reduced Costs: Smart manufacturing optimizes resource allocation, reduces energy consumption, and minimizes waste.
- Increased Competitiveness: Smart manufacturing enables businesses to stay competitive in the global market by offering innovative products, services, and experiences.
Challenges and Limitations: - High Initial Investment: Implementing smart manufacturing technologies requires significant upfront investments in hardware, software, and training.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating different systems, devices, and data sources can be complex and time-consuming.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Smart manufacturing introduces new cybersecurity risks due to the increased connectivity and data exchange between devices and systems.
- Skills Gap: The adoption of smart manufacturing requires a significant shift in workforce skills, which can be challenging for companies to implement.
Future Directions:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML will play an increasingly important role in optimizing production processes, predicting maintenance needs, and improving product quality.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT will continue to expand its presence in manufacturing, enabling real-time monitoring, remote access, and predictive maintenance.
- 5G Networks: 5G networks will provide faster data transfer rates, lower latency, and increased connectivity, enabling more widespread adoption of smart manufacturing technologies.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Smart manufacturing will prioritize environmental sustainability by reducing waste, conserving resources, and promoting eco-friendly practices throughout the product lifecycle.
Evolution of Digital Manufacturing
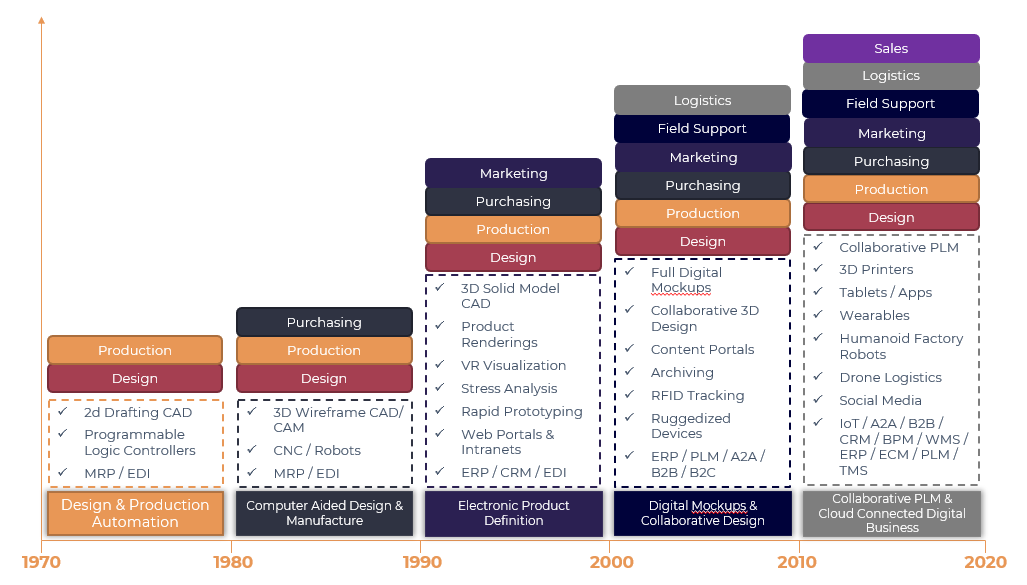 Digital manufacturing has revolutionized the way products are designed, manufactured, and delivered. From its humble beginnings in the 1970s to the present day, digital manufacturing has evolved significantly, driven by advances in technology, changing business needs, and shifting consumer demands.
Digital manufacturing has revolutionized the way products are designed, manufactured, and delivered. From its humble beginnings in the 1970s to the present day, digital manufacturing has evolved significantly, driven by advances in technology, changing business needs, and shifting consumer demands.
Notable Milestones
- The Early Days of Digital Manufacturing
- Digital manufacturing began in the 1970s with the introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) software. CAD allowed designers to create detailed designs on computers, replacing traditional drafting methods. This marked the beginning of a new era in product development, enabling faster and more accurate design iterations.
- The Rise of Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM)
- In the 1980s, computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) emerged as a natural extension of CAD. CAM software enabled manufacturers to create detailed instructions for machine tools, automating many production processes. This led to significant improvements in productivity and efficiency.
- The Advent of Digital Mockups
- The 1990s saw the introduction of digital mockups, which allowed designers to create virtual prototypes of products or systems. This enabled faster testing and validation of designs, reducing the need for physical prototypes and accelerating time-to-market.
- Collaborative Design and Manufacturing
- In the 2000s, collaborative design and manufacturing became increasingly important. Digital platforms enabled global teams to work together seamlessly, sharing data and expertise in real-time. This led to significant improvements in product quality, reducing errors and defect
- The Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0
- The 2010s saw the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0. IoT enabled the integration of sensors, actuators, and other devices into products and systems, creating a new level of connectivity and automation. Industry 4.0 built on this foundation, introducing advanced manufacturing technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity.
Impact on Industry
- The evolution of digital manufacturing has had a profound impact on various industries, including:
- Reduced production costs: Automation and digitalization have led to cost savings and increased efficiency.
- Improved product quality: Digital tools enable precise design and manufacturing, resulting in higher-quality products.
- Enhanced collaboration: Global teams can collaborate more effectively using digital mockups and collaborative design tools.
- Increased speed-to-market: Rapid prototyping and testing capabilities have accelerated the development cycle.
Future of Digital Manufacturing
- As we look to the future, digital manufacturing will continue to evolve rapidly. Emerging trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI will play an increasingly important role in product development, enabling designers to create more complex and sophisticated products.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology will provide a secure and transparent way to track products throughout their lifecycle.
- 5G Networks: 5G networks will enable faster and more reliable connectivity, supporting the growth of IoT and Industry 4.0.
Discrete vs Process Manufacturing
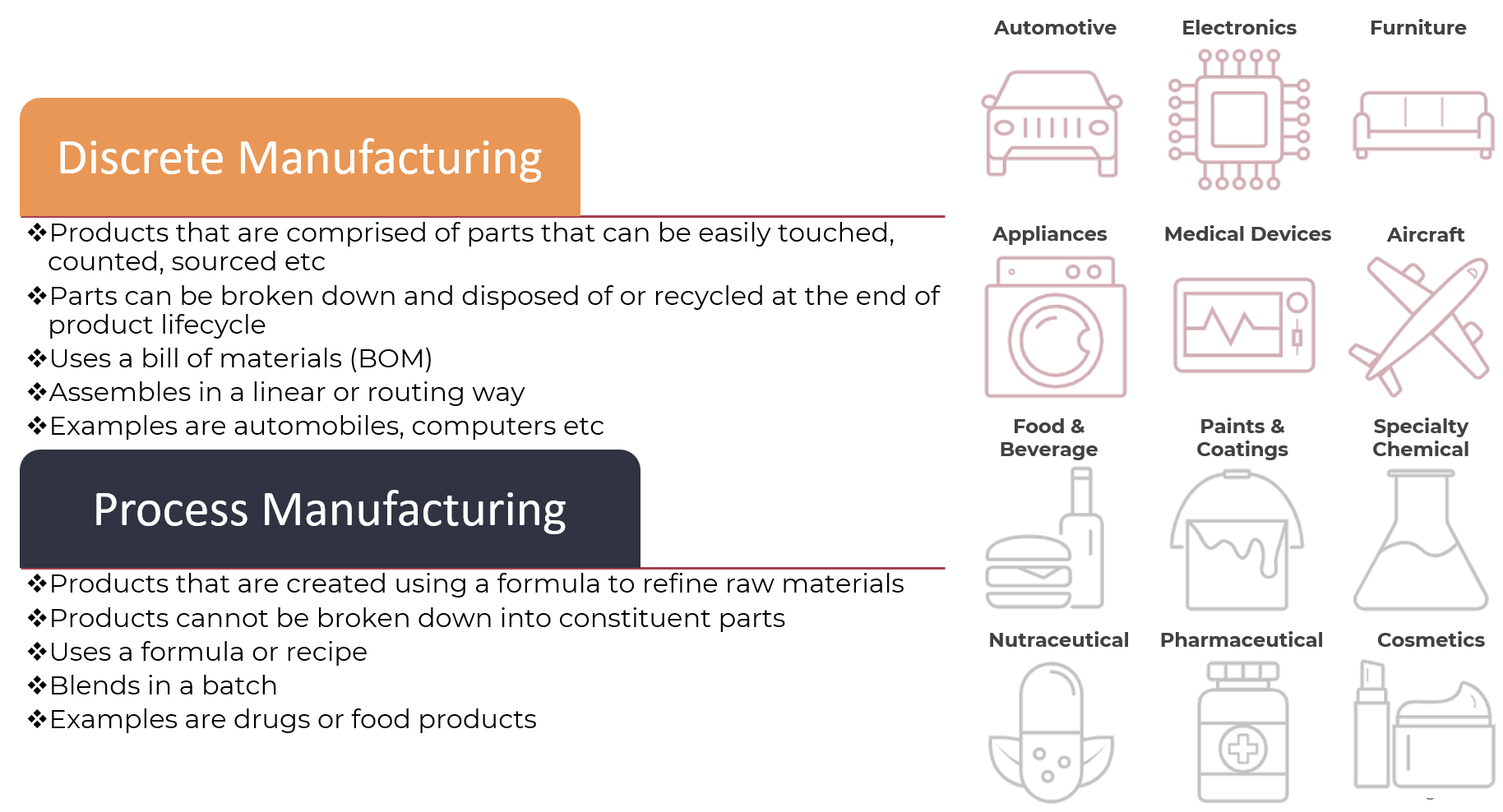
Discrete Manufacturing
- Definition
- Discrete manufacturing involves creating products that are comprised of parts that can be easily touched, counted, sourced, or broken down at the end of their product lifecycle. This type of manufacturing is characterized by the production of individual units or components that are assembled together to form a final product.
- Characteristics
- Products are made up of discrete components
- Parts can be broken down and recycled at the end of their product lifecycle
- Benefits
- Flexibility in production planning and scheduling
- Ability to produce complex products with multiple parts
- High level of control over the production process
- Challenges
- Higher upfront costs due to specialized equipment and training
- Increased risk of errors or defects during production
- Limited flexibility in responding to changes in market demand
- Industry Examples
- Automotive industry: discrete manufacturing is used to produce individual components such as engines, transmissions, and chassis.
- Electronics industry: discrete manufacturing is used to produce individual components such as microprocessors, memory chips, and circuit boards.
Process Manufacturing
- Definition
- Process manufacturing involves transforming raw materials into intermediate goods through various processes. This type of manufacturing is characterized by the production of large quantities of standardized products using continuous processing techniques.
- Characteristics
- Products are created through a series of chemical or physical transformations
- Raw materials are transformed into intermediate goods through various processes
- Benefits
- High level of efficiency and productivity due to automation and continuous processing
- Ability to produce large quantities of standardized products quickly and efficiently
- Lower upfront costs compared to discrete manufacturing
- Challenges
- Limited flexibility in responding to changes in market demand
- Higher risk of errors or defects during production due to complex processes
- Dependence on raw materials and suppliers
- Industry Examples
- Pharmaceutical industry: process manufacturing is used to transform raw materials into intermediate goods such as APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients) and finished dosage forms.
- Food processing industry: process manufacturing is used to transform raw ingredients into final products such as beverages, snacks, and prepared meals.
Key Capabilities
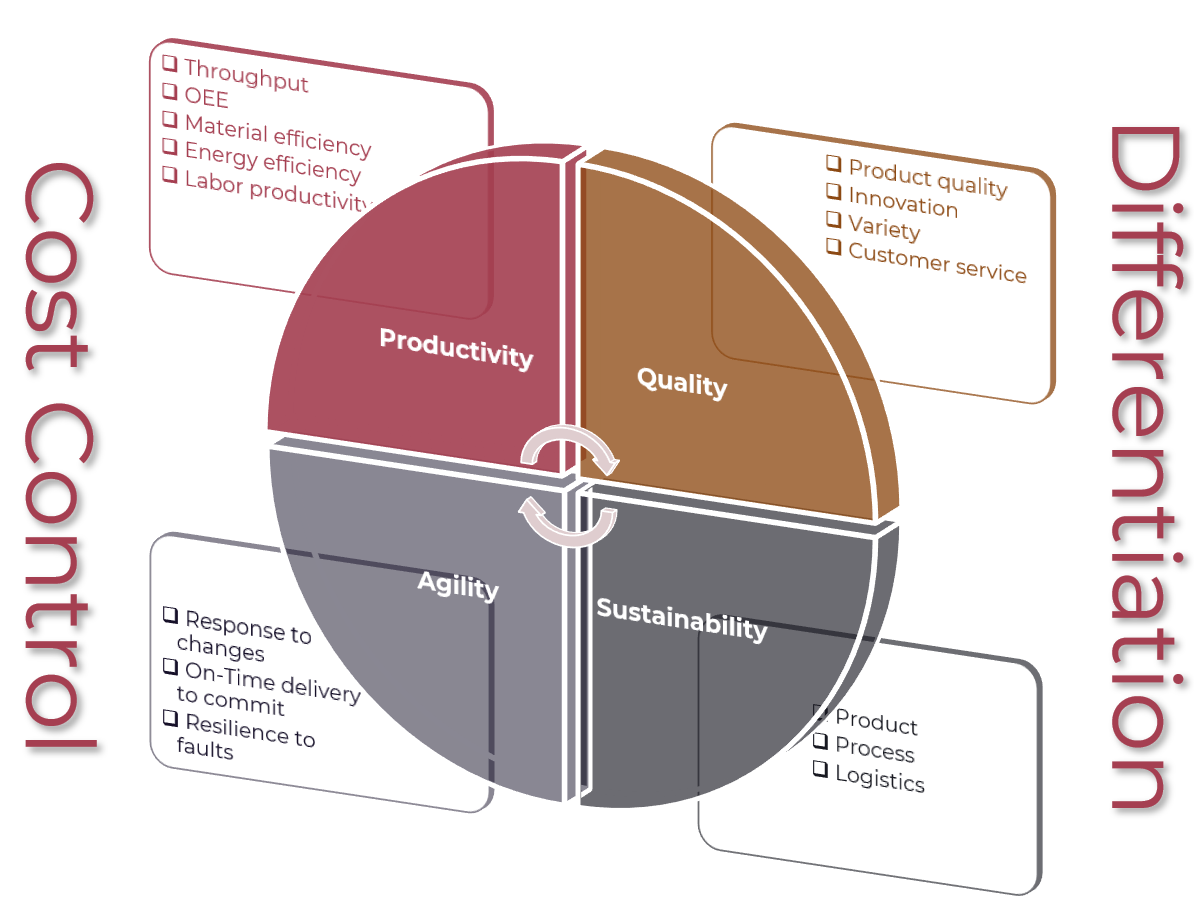
Smart Manufacturing is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various aspects of production, including cost control and differentiation through four key areas: Productivity, Quality, Agility, and Sustainability. These dimensions are interconnected and interdependent, working together to drive innovation, efficiency, and competitiveness in the manufacturing sector. By understanding these perspectives, businesses can better navigate the complexities of smart manufacturing and make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals
Cost Control
- Economic Benefits: Customers are looking for cost-effective solutions that can help them save money on operational expenses.
- This includes reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and optimizing resource allocation.
- By implementing smart manufacturing technologies, customers can achieve significant cost savings and improve their bottom line.
- Efficiency and Productivity: Customers want to see improvements in efficiency and productivity, as this will enable them to produce more with less effort and resources.
- This includes streamlining processes, reducing downtime, and increasing throughput.
- By leveraging smart manufacturing technologies, customers can achieve greater efficiency and productivity, leading to increased competitiveness and profitability.
- Innovation and Efficiency: Customers are interested in innovative solutions that can help them stay ahead of the competition.
- This includes adopting new technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- By embracing these innovations, customers can gain a competitive edge and improve their overall performance.
Differentiation
- Quality and Reliability: Customers place a high value on quality and reliability in their products.
- This includes ensuring that products meet or exceed customer expectations in terms of performance, durability, and safety.
- By implementing smart manufacturing technologies, customers can achieve higher levels of quality and reliability, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Customization and Flexibility: Customers are looking for manufacturers who can offer customized solutions tailored to their specific needs.
- This includes providing flexible production processes that can accommodate changes in demand or product requirements.
- By leveraging smart manufacturing technologies, customers can achieve greater customization and flexibility, enabling them to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
- Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility: Customers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of their products and operations.
- This includes reducing waste, minimizing energy consumption, and using sustainable materials.
- By implementing smart manufacturing technologies, customers can achieve significant reductions in their environmental footprint, improving their reputation and competitiveness.
Design Principles & Smart System Elements
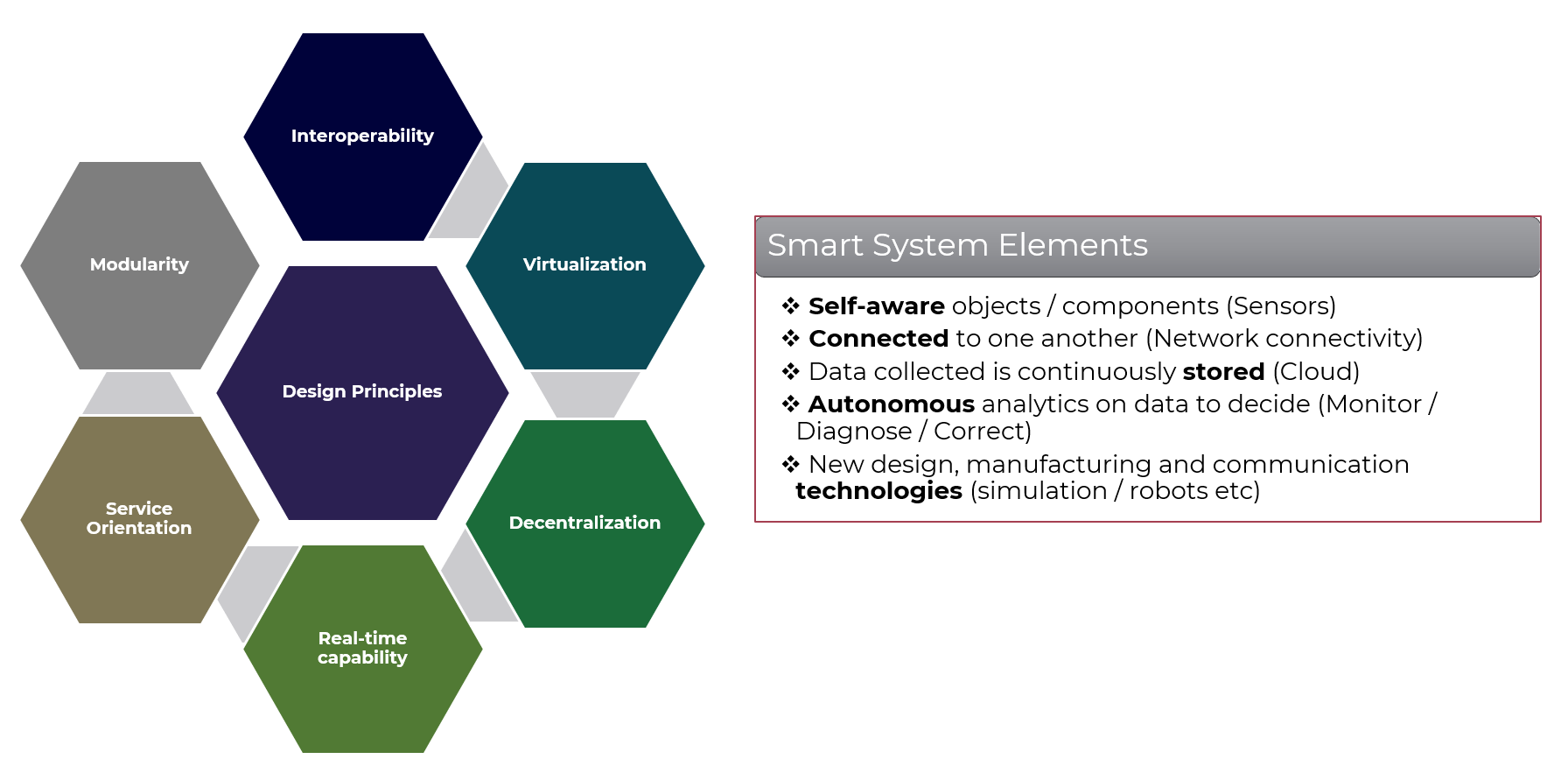 A comprehensive framework for designing and implementing industrial production systems in the modern era.
A comprehensive framework for designing and implementing industrial production systems in the modern era.
Core Components
- Interoperability: This concept refers to the seamless integration and communication between various devices, systems, and software platforms within a manufacturing system. Interoperability enables different components to exchange data and work together efficiently.
- Virtualization: Virtualization involves creating virtual representations of physical assets or processes in a digital environment. It allows for simulations, modeling, and analysis without the need for physical prototypes.
- Decentralization: Decentralized systems distribute decision-making authority among various nodes or components within the system. This approach enhances flexibility, resilience, and adaptability.
Key Principles
- Modularity: Modular systems consist of interchangeable components that can be easily reconfigured or replaced. This design principle promotes flexibility and reduces waste.
- Service orientation: Smart manufacturing emphasizes providing services rather than just products. This approach enables businesses to offer customized solutions, enhance customer experience, and create new revenue streams.
Smart System Elements
- Self-awareness/ Autonomy: Smart manufacturing systems are equipped with sensors and data analytics capabilities that enable them to monitor their own performance and make adjustments in real-time
- Connectivity: These systems are connected through various networks (e.g., IoT, cloud computing) to facilitate data exchange and collaboration among different stakeholders.
- Data-driven decision-making: Smart manufacturing relies heavily on data analysis and AI algorithms to optimize production processes, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall efficiency.
- Autonomous analytics on data to decide (Monitor / Diagnose / Correct): These systems use AI-powered tools to analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, enabling them to identify issues, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes.
- New design, manufacturing and communication technologies: Smart manufacturing incorporates cutting-edge technologies like 3D printing, augmented reality (AR), and the Internet of Things (IoT) to streamline operations, improve product quality, and enhance collaboration among stakeholders.
Ecosystem
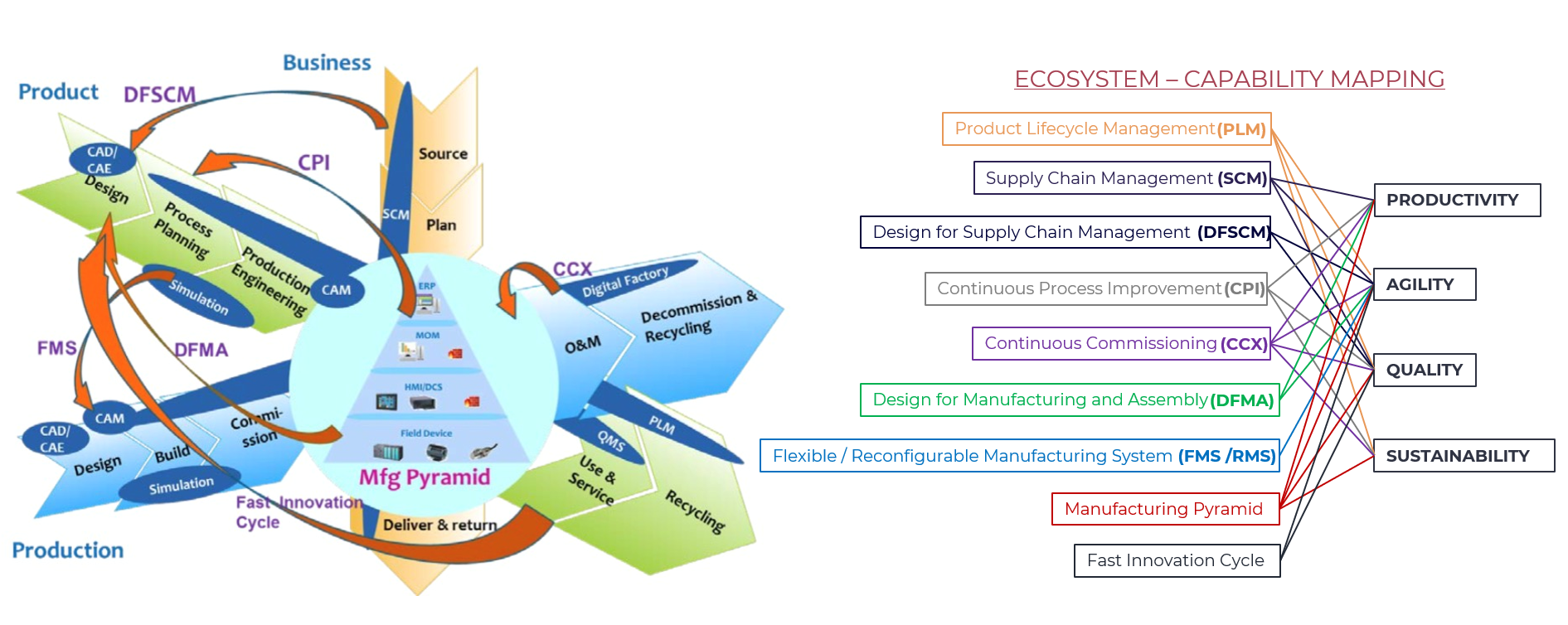
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
- PLM is a set of business processes and tools that enable companies to design, manufacture, and manage products throughout their lifecycle.
- Capability Mapping:
- Agility: PLM enables rapid product development and iteration, allowing companies to quickly respond to changing market conditions.
- Quality: PLM ensures that products meet quality standards by managing data across the entire product lifecycle.
- Sustainability: PLM helps reduce waste and improve resource efficiency by optimizing production processes and supply chains.
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- SCM is a set of activities involved in sourcing, producing, and delivering products to customers.
- Capability Mapping:
- Productivity: SCM optimizes the flow of goods, services, and related information from raw materials to end customers, improving productivity and efficiency.
- Agility: SCM enables rapid response to changing market conditions by streamlining supply chain operations.
- Quality: SCM ensures that products meet quality standards by managing data across the entire supply chain.
Design for Supply Chain Management (DFSCM)
- DFSCM is a design approach that considers the impact of product design on supply chain operations and costs
- Capability Mapping:
- Agility: DFSCM enables rapid response to changing market conditions by designing products that are easy to manufacture and distribute.
- Quality: DFSCM ensures that products meet quality standards by considering the impact of design on supply chain operations.
Continuous Process Improvement (CPI)
- CPI is a methodology for ongoing improvement of business processes based on data-driven insights.
- Capability Mapping:
- Productivity: CPI identifies areas for process optimization, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
- Quality: CPI ensures that products meet quality standards by continuously monitoring and improving production processes.
- Sustainability: CPI helps reduce waste and improve resource efficiency by optimizing production processes and supply chains.
Continuous Commissioning (CCX)
- CCX is a methodology for ongoing improvement of industrial operations based on data-driven insights
- Capability Mapping:
- Productivity: CCX identifies areas for process optimization, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
- Agility: CCX enables rapid response to changing market conditions by streamlining production processes.
- Quality: CCX ensures that products meet quality standards by continuously monitoring and improving production processes.
- Sustainability: CCX helps reduce waste and improve resource efficiency by optimizing production processes and supply chains.
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA)
- DFMA is a design approach that considers the impact of product design on manufacturing and assembly operations and cost
- Capability Mapping:
- Productivity: DFMA enables rapid response to changing market conditions by designing products that are easy to manufacture and assemble.
- Agility: DFMA ensures that products meet quality standards by considering the impact of design on manufacturing and assembly operations.
Flexible / Reconfiguration Manufacturing System (FMS/RMS)
- FMS/RMS is a system that enables rapid reconfiguration of production lines to respond to changing market conditions.
- Capability Mapping:
- Agility: FMS/RMS enables rapid response to changing market conditions by streamlining production processes.
Manufacturing Pyramid
- Manufacturing pyramid is a framework for designing and implementing industrial production systems that are highly efficient, agile, and adaptable.
- Capability Mapping:
- Productivity: Manufacturing pyramid optimizes the flow of goods, services, and related information from raw materials to end customers, improving productivity and efficiency.
- Agility: Manufacturing pyramid enables rapid response to changing market conditions by streamlining production processes.
- Quality: Manufacturing pyramid ensures that products meet quality standards by managing data across the entire supply chain.
- Sustainability: Manufacturing pyramid helps reduce waste and improve resource efficiency by optimizing production processes and supply chains.
Fast Innovation Cycle
- Fast innovation cycle is a methodology for rapid product development and iteration, enabling companies to quickly respond to changing market conditions.
- Capability Mapping:
- Agility: Fast innovation cycle enables rapid response to changing market conditions by streamlining production processes.
- Quality: Fast innovation cycle ensures that products meet quality standards by continuously monitoring and improving production processes.
Landscape
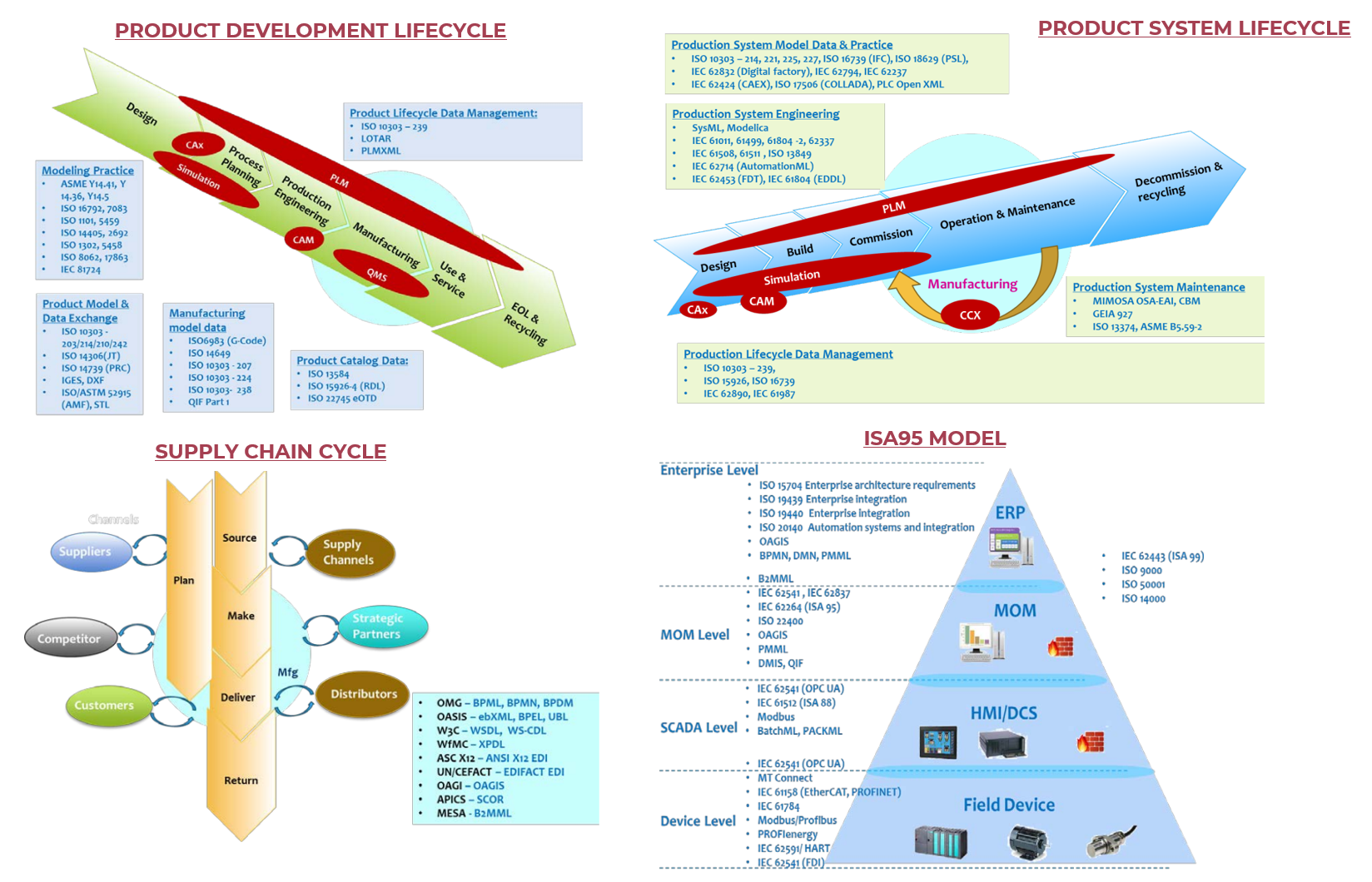
Product Development Lifecycle
- Design: The design phase involves creating detailed specifications for a product or system, including its functionality, performance, and aesthetics.
- Manufacturing: In the manufacturing stage, raw materials are transformed into the final product using various processes such as machining, assembly, and testing.
- Installation: Once the product is manufactured, it must be installed in the customer’s facility. This may involve on-site installation, training, and commissioning.
- Maintenance: After installation, products require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and extend their lifespan.
- Disposal: Eventually, products reach the end of their life cycle and need to be disposed of responsibly.
Product System Lifecycle
- Design: Similar to the product development lifecycle, design in the product system lifecycle focuses on creating specifications for a system or solution that meets specific needs.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing involves producing the components or subsystems that make up the system.
- Installation: Installation is similar to the product development lifecycle, with a focus on setting up and configuring the system.
- Maintenance: Maintenance ensures the system operates efficiently and effectively over time
- Disposal: Disposal refers to the responsible removal of the system at the end of its useful life.
Supply Chain Cycle
- Planning: Supply chain planning involves forecasting demand, managing inventory, and optimizing logistics to ensure timely delivery of products or services.
- Sourcing : Sourcing encompasses activities such as procurement, supplier management, and quality control to secure raw materials or components.
- Production: Production refers to the manufacturing process that transforms raw materials into finished goods.
- Distribution: Distribution involves transporting products from the manufacturer to customers through various channels such as wholesalers, retailers, or e-commerce platforms.
- Returns: Returns management ensures efficient handling of customer returns, including processing, inspection, and restocking
ISA95 Model
- Enterprise Level: The enterprise level encompasses business processes, organizational structures, and systems that support overall operations.
- Manufacturing Execution System (MES): MES manages the production floor, overseeing activities like batch management, quality control, and scheduling.
- Control Systems: Control systems monitor and control equipment, machines, and processes within the manufacturing environment.
- Device Level: Device level refers to individual devices or components used in production, such as sensors, actuators, and robots.
Standard Opportunities
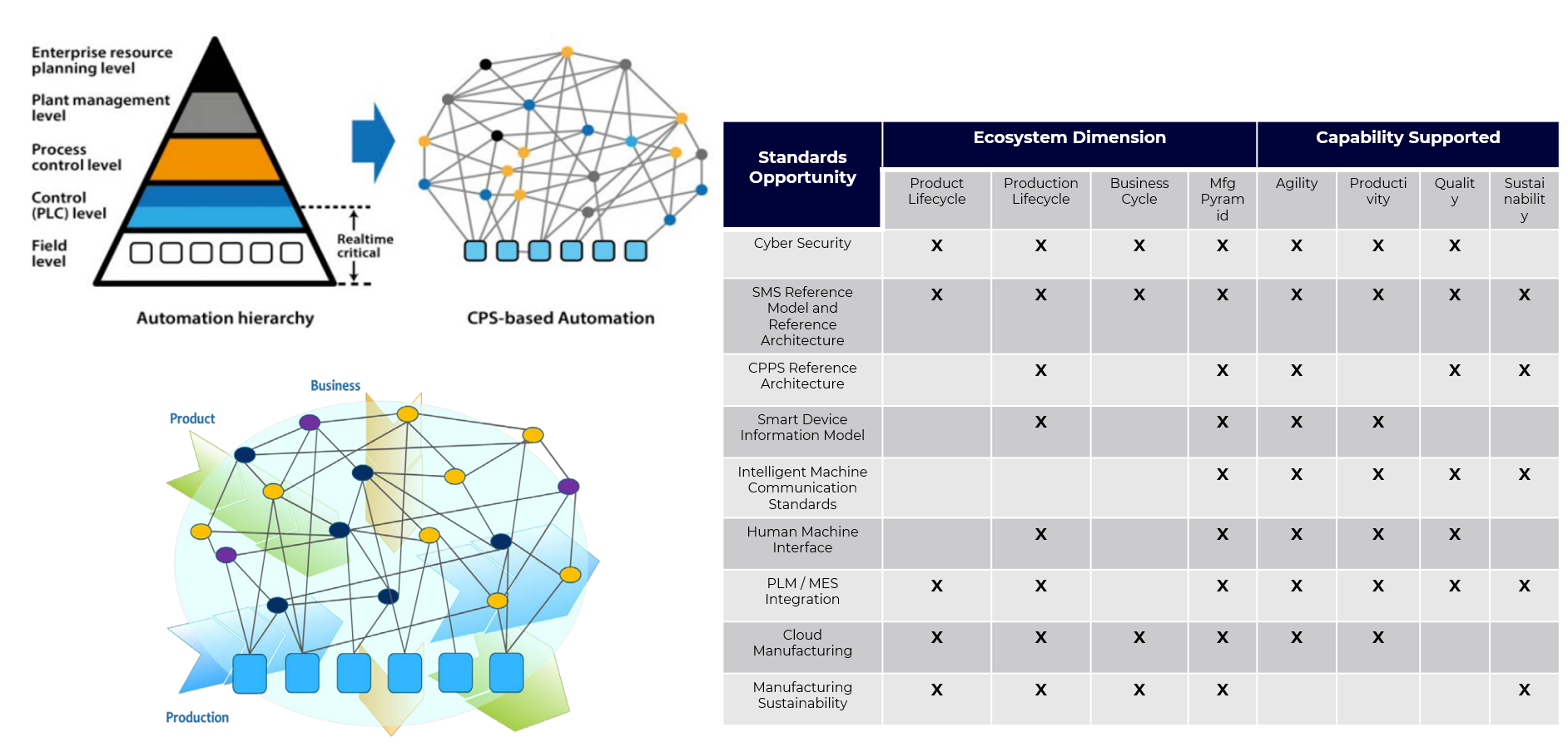
Cyber Security
- The rise of Industry 4.0 has led to the increasing use of cyber-physical systems (CPS) and industrial internet of things (IIoT) devices, which are connected to the Internet and can be accessed remotely.
- This connectivity creates new opportunities for hackers to attack these systems and cause significant damage.
- Threats
- Malware: Viruses, worms, and Trojans that can compromise system security.
- Phishing attacks: Scammers use social engineering tactics to trick employees into revealing sensitive information or gaining access to the network.
- Ransomware: Hackers encrypt data and demand payment in exchange for the decryption key.
- DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-Service) attacks: Overwhelming a system with traffic from multiple sources, making it unavailable to users.
- Countermeasures
- Implementing robust security protocols such as encryption, secure authentication methods, and access controls.
- Conducting regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities.
- Providing employee training on cybersecurity best practices and phishing awareness.
- Installing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
SMS Reference Model and Reference Architecture
- The SMS reference model provides a framework for designing and implementing smart manufacturing systems.
- It enables the integration of various technologies such as sensors, actuators, and automation devices into a single platform.
- Key Components
- Sensor data management: Collecting and processing sensor data from various sources to provide real-time insights into production processes.
- Data analytics: Analyzing data to identify trends, patterns, and correlations that can inform decision-making.
- Automation control: Implementing automation systems to streamline manufacturing processes and improve efficiency.
- Benefits
- Improved productivity: By automating routine tasks, companies can increase their output while reducing labor costs.
- Enhanced quality: Real-time monitoring of production processes allows for quick detection and correction of defects.
- Reduced waste: Automation helps minimize waste by optimizing material usage and reducing scrap rates.
CPPS Reference Architecture
- The CPPS reference architecture is designed to support the integration of physical systems with cyber-physical systems (CPS).
- It enables seamless communication between devices, humans, and data analytics tools.
- Key Components
- Physical layer: This layer represents the physical components of the system, such as sensors, actuators, and automation devices.
- Cyber layer: This layer represents the cyber-physical systems (CPS) that interact with the physical layer.
- Application layer: This layer represents the applications and services that run on top of the cyber layer.
- Benefits
- Improved efficiency: By integrating physical and cyber components, companies can streamline their manufacturing processes and reduce costs.
- Enhanced flexibility: CPPS enable real-time monitoring and control of production processes, allowing for quick responses to changes in market demand.
- Better decision-making: Data analytics tools provide insights into production processes, enabling informed decision-making.
Smart Device Information Model
- The Smart Device Information Model (SDIM) is a standardized framework for representing and exchanging information about smart devices.
- It enables seamless integration of devices from different manufacturers and facilitates interoperability between systems.
- Key Components
- Device description: A standardized way to describe the characteristics, capabilities, and behavior of a device.
- Data model: A structured representation of the data exchanged between devices and applications.
- Interface definition: A standardized interface for interacting with devices, including protocols and APIs.
- Benefits
- Improved interoperability: Devices from different manufacturers can be integrated into a single system.
- Enhanced scalability: The SDIM enables the easy addition of new devices to an existing system.
- Better decision-making: Standardized data models provide insights into device performance and behavior.
Intelligent Machine Communication Standards
- Intelligent machines are increasingly being used in manufacturing to improve efficiency and productivity.
- However, these machines often require complex communication protocols to interact with other devices and systems.
- Key Components
- Device-level communication: Protocols for interacting with individual devices, such as sensors and actuators.
- Machine-to-machine (M2M) communication: Protocols for interacting between intelligent machines, enabling real-time coordination and collaboration.
- Human-machine interface (HMI): Protocols for interacting with humans, including user interfaces and control systems.
- Benefits
- Improved efficiency: Intelligent machines can optimize production processes in real-time. Enhanced flexibility: M2M communication enables the easy reconfiguration of production lines to respond to changing market demand.
Human Machine Interface
- The Human Machine Interface (HMI) is the layer that enables humans to interact with intelligent machines and production systems.
- It provides a user-friendly interface for controlling and monitoring production processes in real-time.
- Key Components
- User interface: A graphical or text-based interface for interacting with the system, including menus, buttons, and displays.
- Control panel: A set of controls for adjusting parameters and settings, such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate.
- Monitoring tools: Real-time displays of production metrics, such as throughput, yield, and quality.
- Benefits
- Improved productivity: By providing a user-friendly interface, humans can interact with the system more efficiently.
- Enhanced flexibility: The HMI enables the easy reconfiguration of production lines to respond to changing market demand.
- Better decision-making: Real-time monitoring tools provide insights into production performance and behavior.
PLM / MES Integration
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) are two critical components of smart manufacturing.
- However, they often require complex integration protocols to share data and coordinate activities.
- Key Components
- Data exchange: Standardized protocols for exchanging data between PLM and MES systems, including product information, production plans, and quality metrics.
- Process integration: Protocols for integrating production processes into the PLM system, enabling real-time monitoring and control.
- Decision support tools: Analytics and visualization tools that provide insights into production performance and behavior.
- Benefits
- Improved efficiency: By integrating PLM and MES systems, companies can streamline their production processes and reduce costs.
- Enhanced flexibility: The integrated system enables the easy reconfiguration of production lines to respond to changing market demand.
- Better decision-making: Standardized protocols provide insights into production performance and behavior.
Cloud Manufacturing
- Cloud manufacturing is an emerging paradigm that enables companies to access advanced manufacturing technologies and resources over the cloud.
- It provides a flexible and scalable platform for managing complex production processes.
- Key Components
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): A set of virtualized infrastructure services, including compute, storage, and networking resources.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): A set of development tools and frameworks for building applications, including programming languages, libraries, and APIs.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): A set of software applications that provide specific business functions, such as product design, simulation, and analytics.
- Benefits
- Improved efficiency: Cloud manufacturing enables companies to access advanced technologies and resources on demand, reducing costs and improving productivity.
- Enhanced flexibility: The cloud provides a scalable platform for managing complex production processes, enabling the easy reconfiguration of production lines to respond to changing market demand.
Manufacturing Sustainability
- Manufacturing sustainability refers to the ability of a company to produce goods while minimizing its environmental impact and social responsibility.
- It requires the integration of sustainable practices throughout the entire production process, from design to delivery.
- Key Components
- Sustainable materials: Materials that are sourced in an environmentally responsible manner, such as recycled or biodegradable materials.
- Energy efficiency: Technologies and processes that reduce energy consumption during production, such as LED lighting or energy-efficient motors.
- Waste reduction: Strategies for minimizing waste generation during production, such as recycling or reusing materials.
- Benefits
- Improved reputation: Companies that prioritize sustainability can enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
- Reduced costs: Sustainable practices can reduce waste, energy consumption, and other operational costs.
Nine Pillars
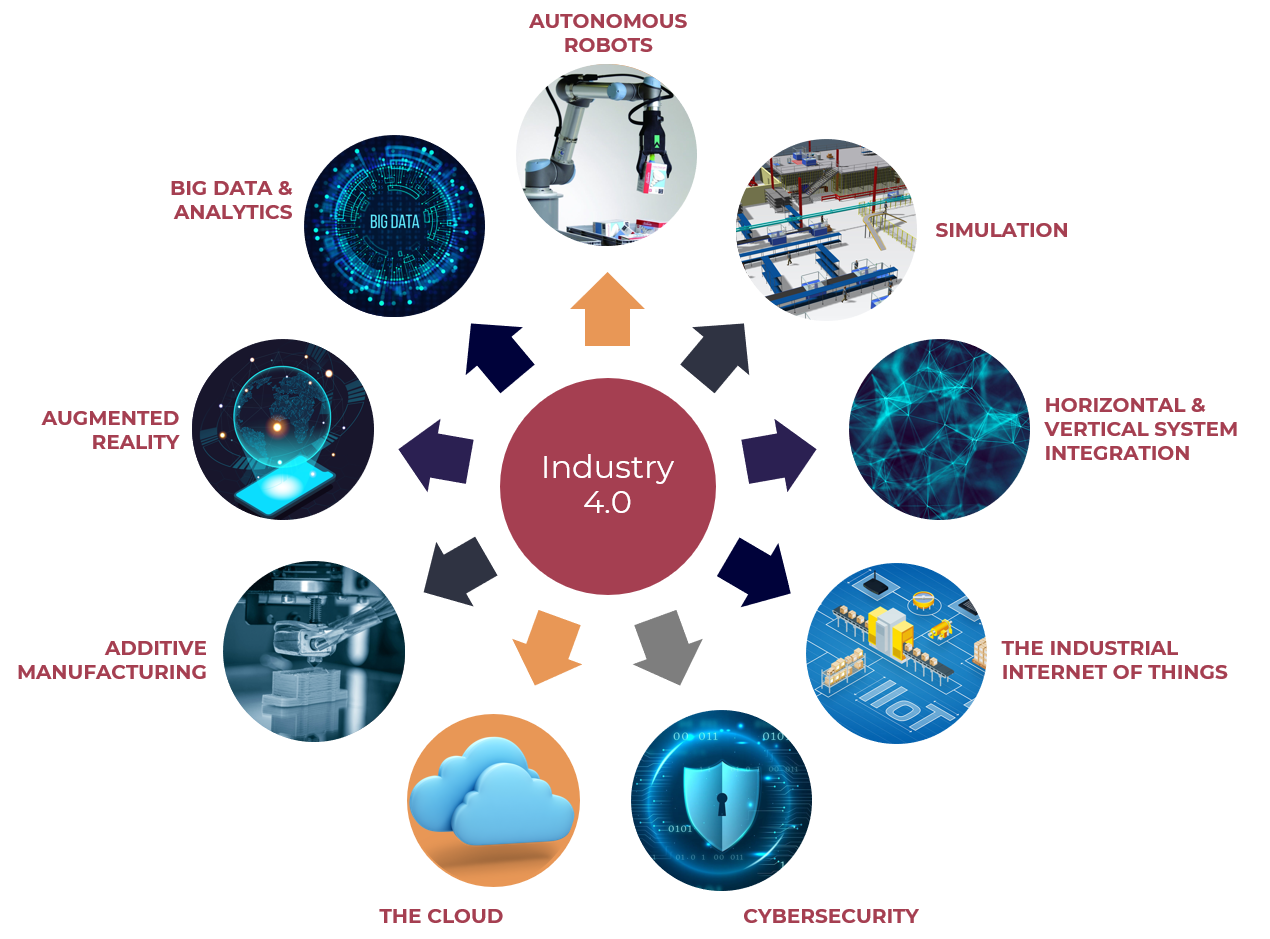 Autonomous Robots: These robots can operate independently without human intervention.
Autonomous Robots: These robots can operate independently without human intervention.
Simulation: This pillar allows for the creation of digital models of physical systems, enabling simulations and analysis.
Horizontal & Vertical System Integration: This involves integrating different layers of a system to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): IIoT enables real-time data collection and analysis from connected devices and sensors.
Cybersecurity: This pillar ensures the protection of industrial systems and data from cyber threats
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing allows for on-demand access to a shared pool of resources, such as servers, storage, and applications.
Additive Manufacturing: Also known as 3D printing, this technology creates complex shapes and structures layer by layer.
Augmented Reality (AR): AR enhances the physical world by overlaying digital information onto it.
Big Data & Analytics: This pillar involves collecting and analyzing large amounts of data to gain insights and make informed decisions.
Additive Manufacturing
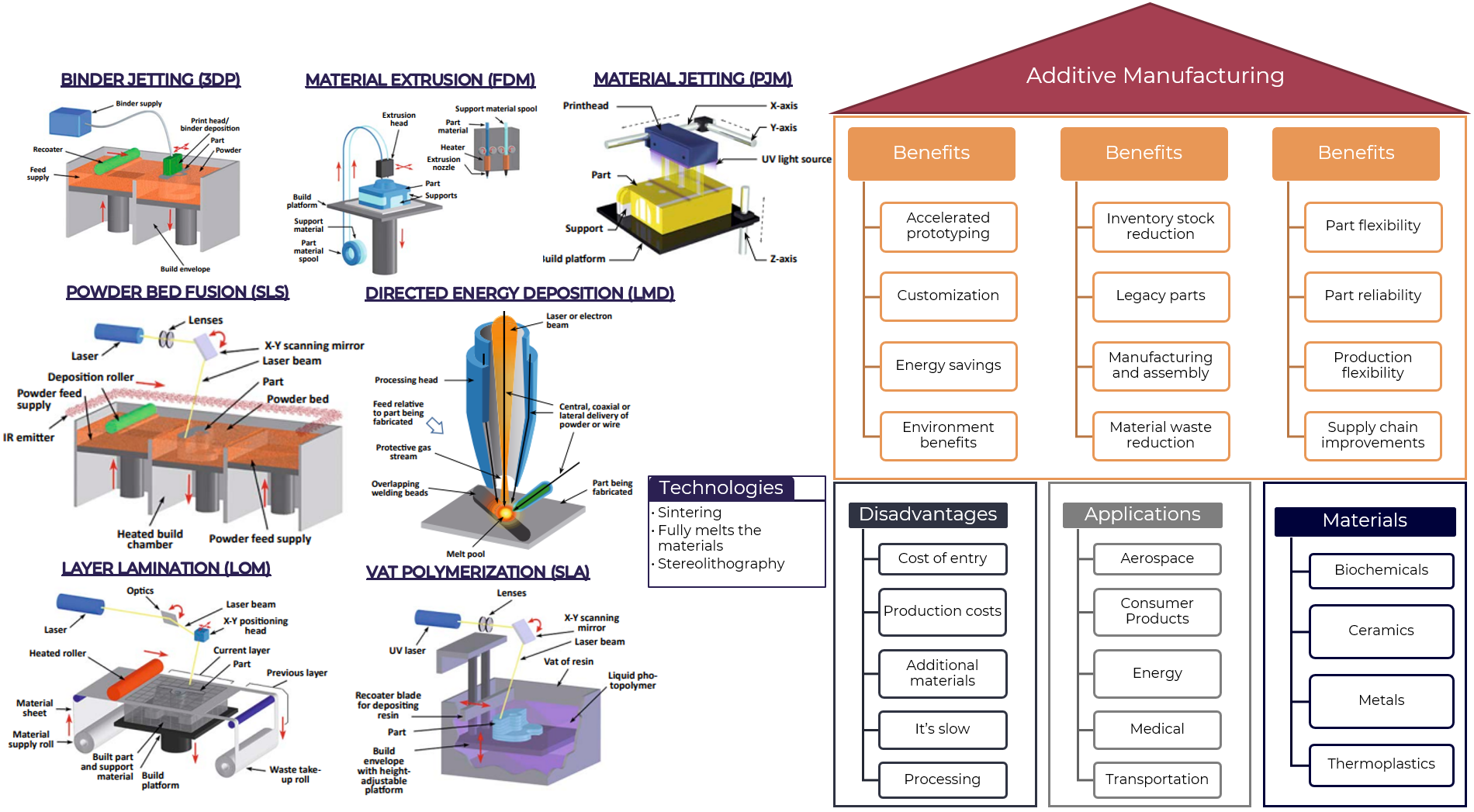
Binder Jetting (3DP)
- Binder jetting is a 3D printing process that uses a liquid binder to “glue” together powder particles. The process works by layering the powder and then using the binder to connect the layers. This method allows for complex geometries and can be used with various materials, including metals and ceramics.
Material Extrusion (FDM)
- Material extrusion is a 3D printing process that uses melted plastic or other materials to create objects layer by layer. The material is fed through a heated nozzle, which extrudes the material onto a build platform. This method is commonly used for prototyping and production of parts with simple geometries.
Material Jetting (PJ)
- Material jetting is a 3D printing process that uses droplets of liquid material to create objects layer by layer. The droplets are deposited through an inkjet printhead, which allows for high-resolution printing. This method is commonly used for printing complex geometries and can be used with various materials, including metals and ceramics.
Directed Energy Deposition (LMD)
- Directed energy deposition (DED) is a 3D printing process that uses a focused beam of energy to melt and deposit metal onto a substrate. The process works by layering the metal powder and then using the beam to fuse the layers together. This method allows for complex geometries and can be used with various metals.
Powder Bed Fusion (SLS)
- Powder bed fusion is a 3D printing process that uses a laser or electron beam to fuse together metal powder layers. The process works by layering the powder and then using the beam to melt the powder particles, creating a solid bond between them. This method allows for complex geometries and can be used with various metals.
Vat Polymerization (SLA)
- Vat polymerization is a 3D printing process that uses ultraviolet light to cure liquid resin layer by layer. The process works by exposing the resin to UV light, which causes it to solidify, creating a solid bond between layers. This method allows for high-resolution printing and can be used with various materials, including plastics and metals
Layer Lamination (LOM)
- Layer lamination is a 3D printing process that uses sheets of material, such as paper or plastic, to create objects layer by layer. The process works by stacking the sheets and then bonding them together using adhesives or heat. This method allows for complex geometries and can be used with various materials, including papers and plastics.
AR / VR / MR / Haptics
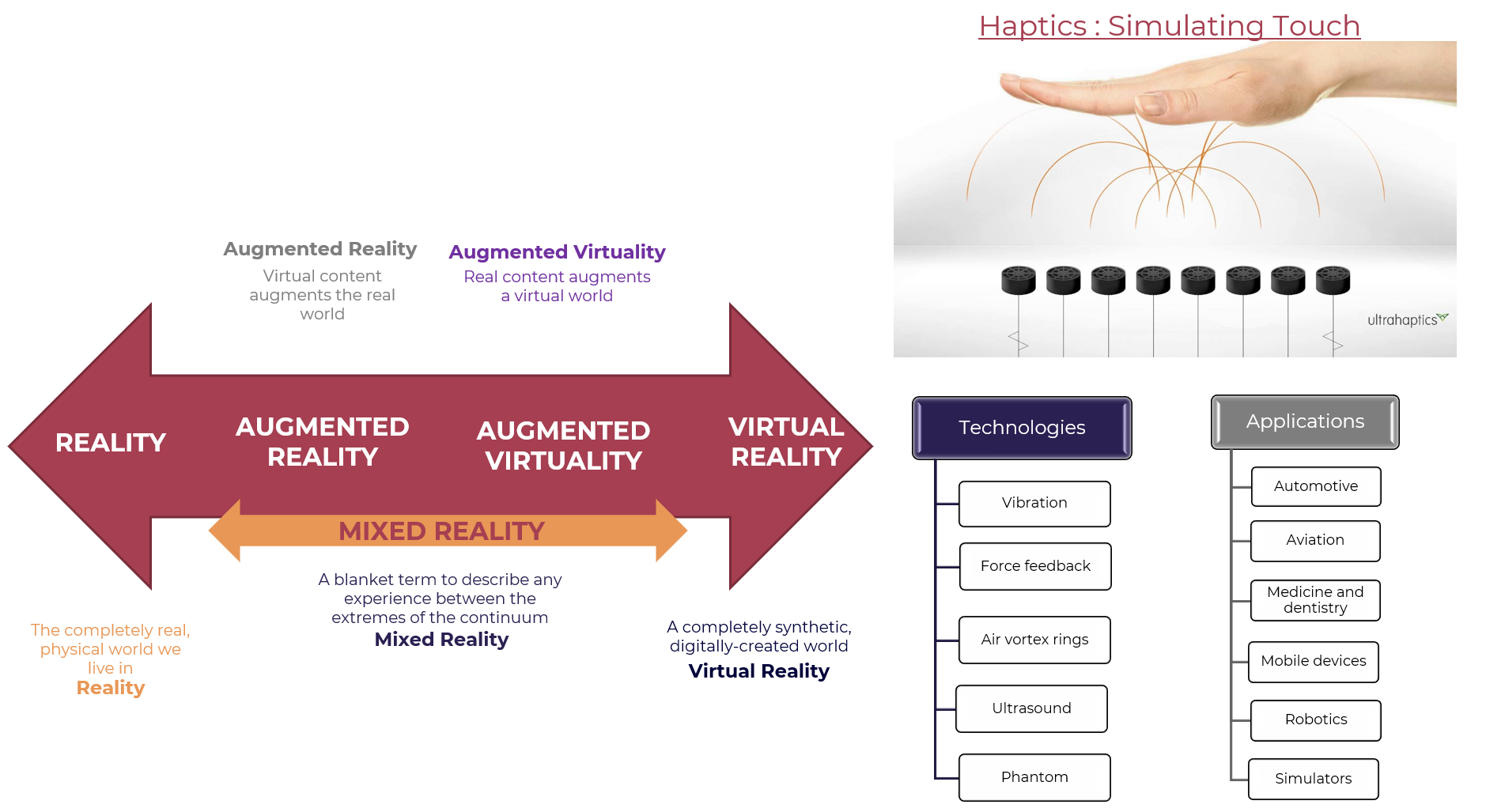
Augmented Reality (AR)
- AR enhances the real world by overlaying digital information onto it.
- It uses visual displays such as smartphones or tablets to project virtual objects or text onto the real environment.
- AR has applications in fields like education, entertainment, and retail.
Virtual Reality (VR)
- VR creates a completely immersive digital environment that simulates reality.
- Users wear special headsets or use other devices to experience virtual worlds.
- VR is used in gaming, training simulations, and therapy
Mixed Reality (MR)
- MR combines elements of both AR and VR to create an interactive environment where the physical world is overlaid with digital information.
- It allows users to interact with virtual objects as if they were real.
- MR has applications in fields like education, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Haptics
- Haptics refers to the sense of touch or feel.
- In the context of AR/VR/MR, haptic technology provides tactile feedback to users, allowing them to interact with virtual objects as if they were real.
- It enhances the overall experience by providing a more realistic and immersive interaction.
Autonomous Robots
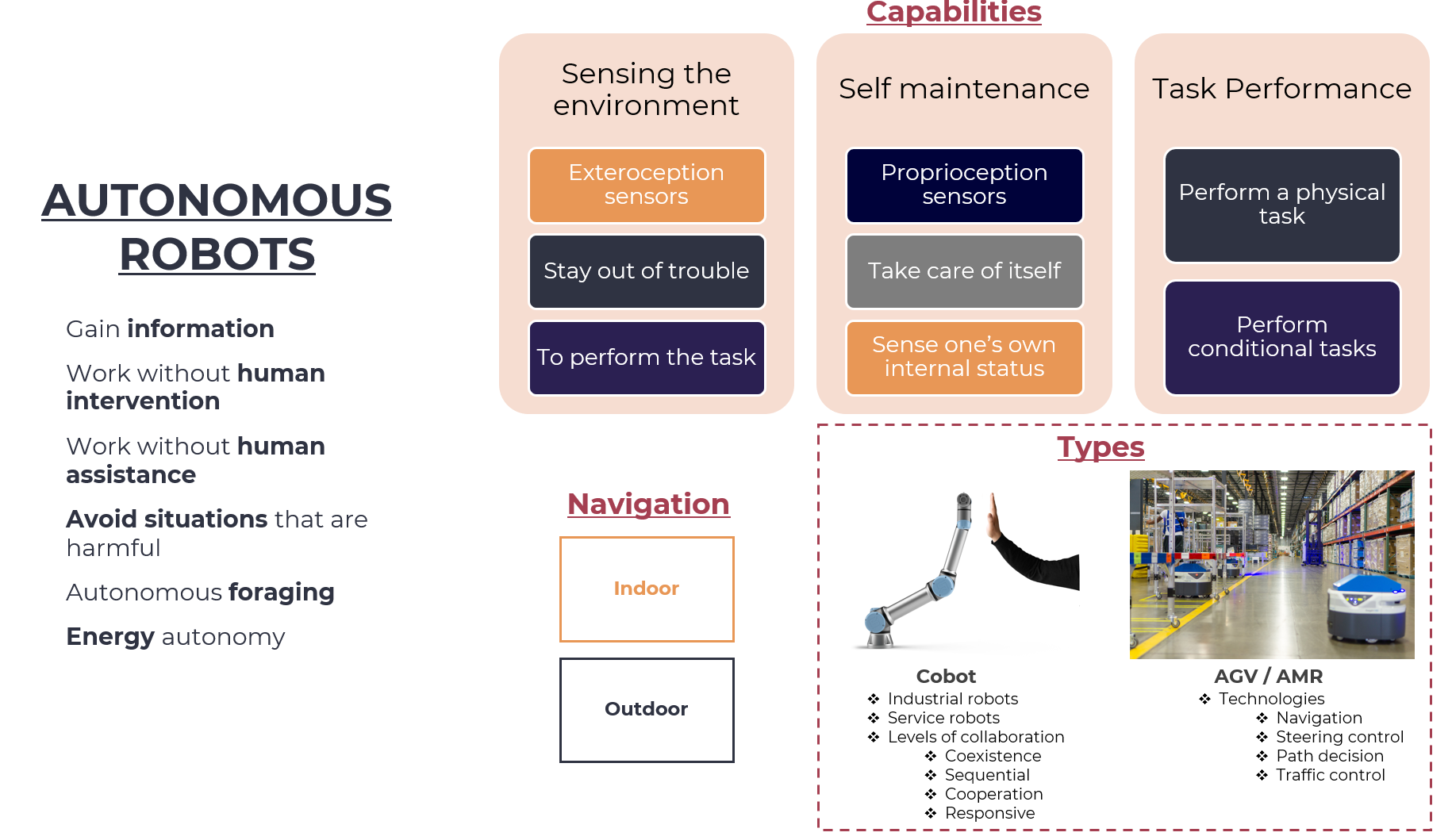
Key Features
- Sensing: Autonomous robots can perceive and respond to their surroundings using various sensors such as cameras, lidars, and radar.
- Navigation: They can navigate through complex environments with ease, avoiding obstacles and finding the most efficient paths to their destinations.
- Task Performance: Autonomous robots can perform a wide range of tasks including assembly, welding, inspection, and quality control.
- Adaptability: They can adapt to changes in production processes, such as new products or manufacturing lines.
Benefits
- Increased Efficiency: Autonomous robots can work around the clock without breaks or downtime, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
- Improved Quality: They can perform tasks with high precision and accuracy, reducing defects and improving product quality.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Autonomous robots can replace human workers in certain tasks, reducing labor costs and improving safety.
Challenges
- Complexity of Integration: Integrating autonomous robots into existing manufacturing systems can be complex and require significant investment.
- Dependence on Data Quality: The accuracy of data collected by sensors and cameras is crucial for the performance of autonomous robots, but errors in data quality can impact their effectiveness.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Autonomous robots may pose cybersecurity risks if not properly secured.
The Cloud
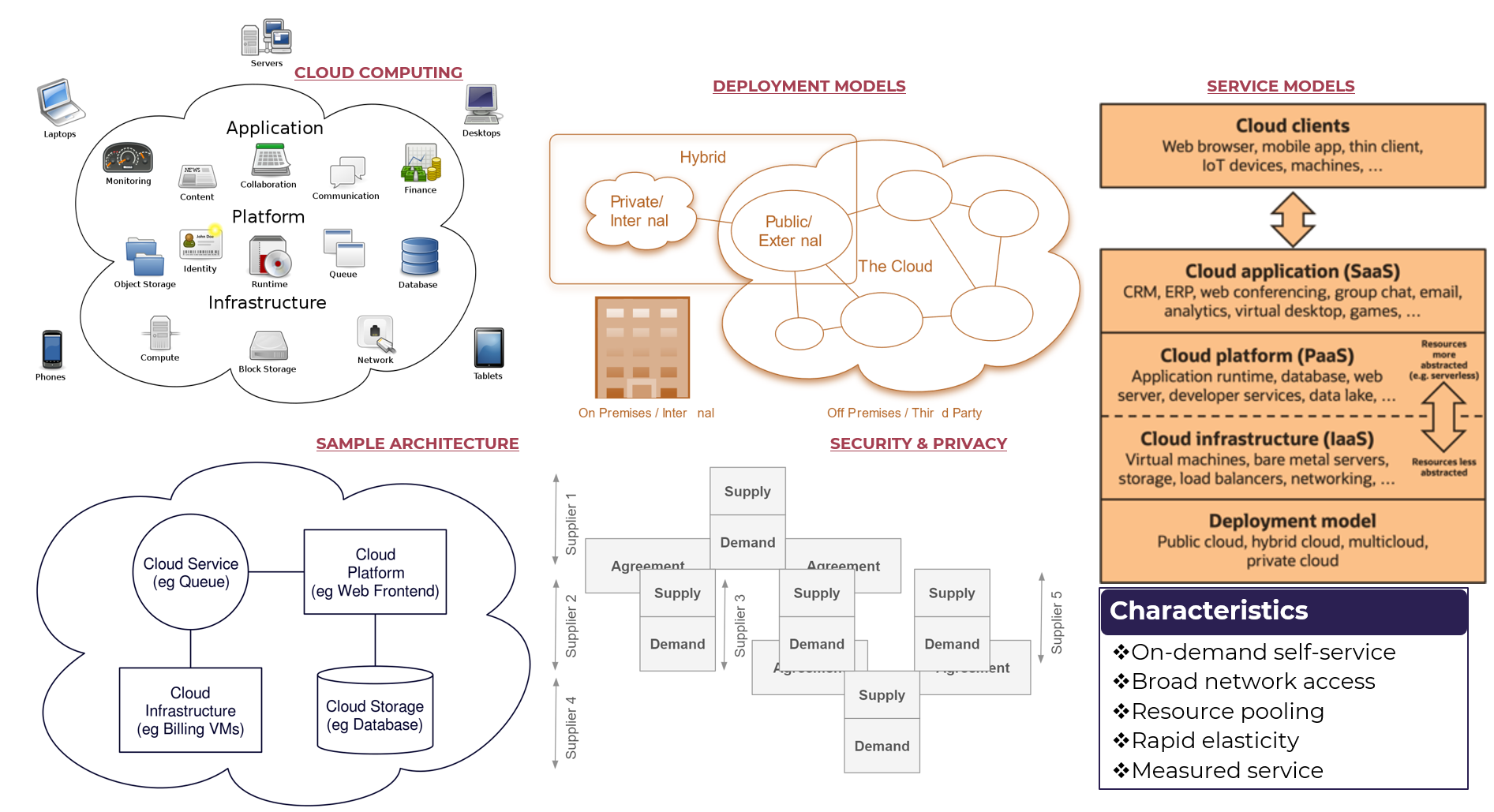
Cloud Computing
- Application: This layer includes various applications such as monitoring, collaboration, communication, finance, and desktops.
- Platform: The platform layer consists of infrastructure, identity management, runtime, queue, database, network, and block storage.
- Infrastructure: This layer encompasses laptops, phones, servers, and desktops.
Deployment Models
- Hybrid: A hybrid model combines on-premises and off-premises environments to provide flexibility and scalability.
- Public/External: In a public cloud, resources are provided over the internet by third-party providers, offering scalability and cost-effectiveness.
- Private/Internal: Private clouds are dedicated to a single organization, providing control and security while still benefiting from economies of scale.
- Community: Community clouds serve multiple organizations with shared interests or objectives, promoting collaboration and resource sharing.
Service Models
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, allowing users to manage their own infrastructure.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): PaaS offers a platform for developing, running, and managing applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance.
Security & Privacy
- Supply: This section highlights the importance of supply chain security in cloud computing, emphasizing the need to ensure that all components are secure.
- Demand: Demand refers to the customer’s requirements and expectations from a cloud service provider, including aspects like performance, availability, and scalability.
- Agreement: An agreement is a legally binding contract between a cloud service provider and its customers, outlining terms and conditions for services rendered.
Characteristics
- On-demand self-service: Cloud computing allows users to provision resources as needed without human intervention.
- Broad network access: Resources are accessible over the internet or private networks from any device with an internet connection.
- Resource pooling: Cloud providers pool their resources to provide a multi-tenant environment, where resources can be allocated and re-allocated efficiently.
- Rapid elasticity: Cloud computing enables rapid scaling up or down based on changing business needs.
- Measured service: Cloud services are metered by the provider, allowing customers to pay only for what they use.
Big Data & Analytics
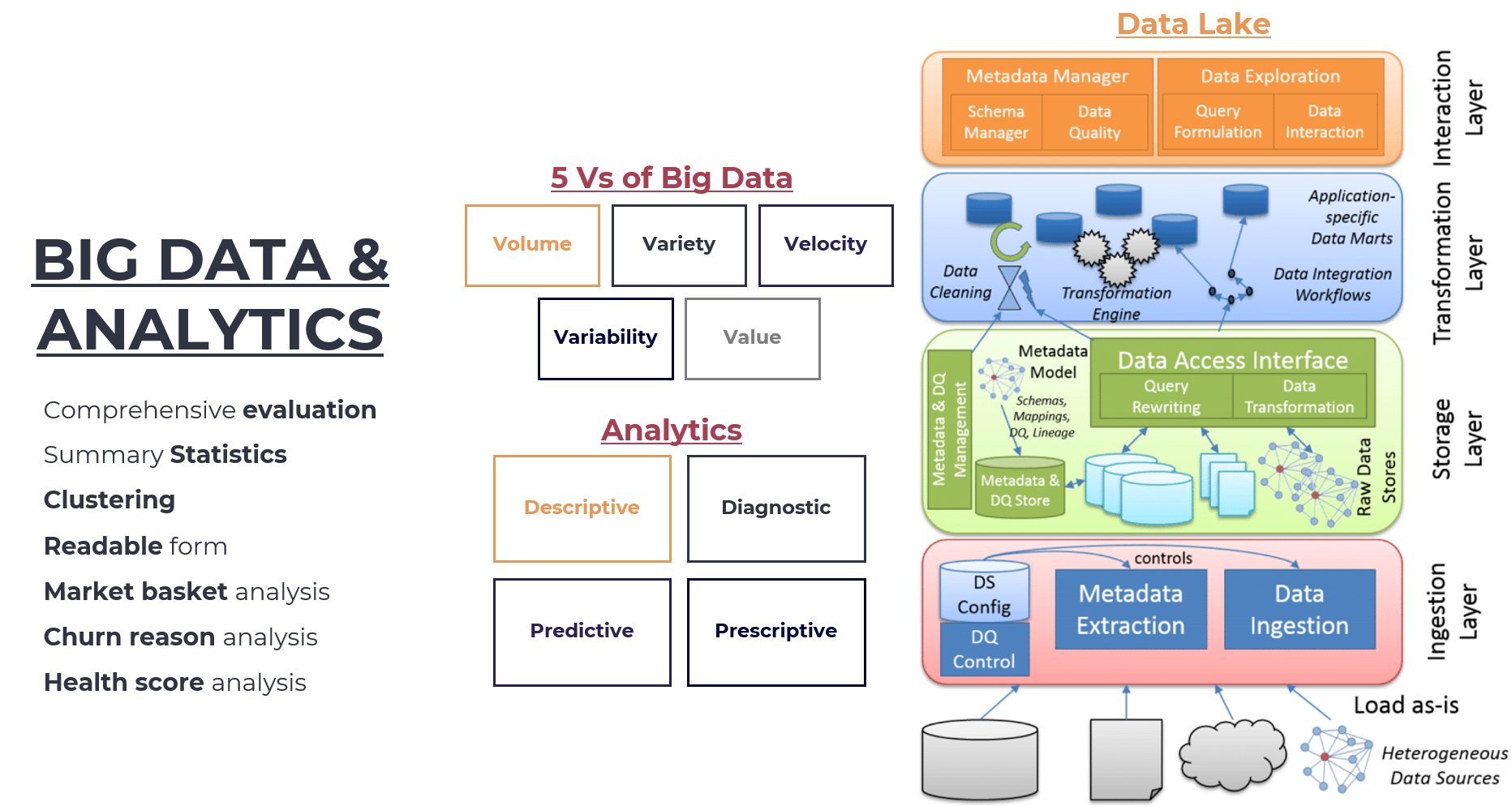 Big Data refers to the vast amounts of structured and unstructured data that organizations generate daily. It has become essential for businesses to manage and analyze this data effectively to gain meaningful insights and make informed decisions
Big Data refers to the vast amounts of structured and unstructured data that organizations generate daily. It has become essential for businesses to manage and analyze this data effectively to gain meaningful insights and make informed decisions
5 Vs of Big Data
- Volume: The sheer amount of data generated by various sources, including social media, sensors, and applications.
- Variety: The different types of data formats, such as structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
- Velocity: The rapid pace at which data is generated and needs to be processed in real-time.
- Value: The ability to extract valuable insights from the data to drive business decisions.
- Veracity: The accuracy and reliability of the data, ensuring that it is trustworthy and reliable.
Analytics
- Descriptive Analytics
- Descriptive analytics is concerned with summarizing historical data to understand what has happened. It provides insights into past events, trends, and patterns within the data.
- Diagnostic Analytics
- Diagnostic analytics involves analyzing descriptive analytics findings to identify root causes of issues or opportunities for improvement.It helps in identifying areas where improvements can be made by understanding why certain outcomes occurred.
- Predictive Analytics
- Predictive analytics utilizes statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future events based on historical data patterns. It enables businesses to anticipate potential outcomes, making informed decisions about investments, resource allocation, and risk management
- Prescriptive Analytics
- Prescriptive analytics takes predictive analytics a step further by providing recommendations for actions to take based on predicted outcomes. It offers actionable insights that guide decision-makers towards optimal solutions, ensuring alignment with business objectives.
Data Lake
- A centralized repository that stores raw, unprocessed data in its native format.It allows for easy data integration, scalability, and flexibility, making it an attractive option for organizations looking to manage large amounts of data
- Layers
- Ingestion Layer
- The Ingestion Layer is responsible for collecting raw, unstructured data from various sources.
- Data Sources: Heterogeneous data sources such as logs, social media feeds, IoT devices, and more.
- Data Format: Raw, unprocessed data in its native format.
- Storage Layer
- The Storage Layer is where the raw data is stored without any processing or transformation.
- Storage Mechanism: A distributed storage system like HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) or object stores like Amazon S3.
- Transformation Layer
- The Transformation Layer is where the raw data is processed and transformed into a structured format for analysis.
- Processing: Data cleaning, filtering, aggregation, and enrichment using ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools or stream processing engines like Apache Storm or Flink.
- Data Format: Structured data in formats like CSV, JSON, or Avro.
- Interaction Layer
- The Interaction Layer is where users interact with the Data Lake to retrieve and analyze processed data.
- Tools and Interfaces: SQL interfaces like Hive or Presto, visual analytics tools like Tableau or Power BI, or machine learning libraries like scikit-learn or TensorFlow.
- Ingestion Layer
Cybersecurity
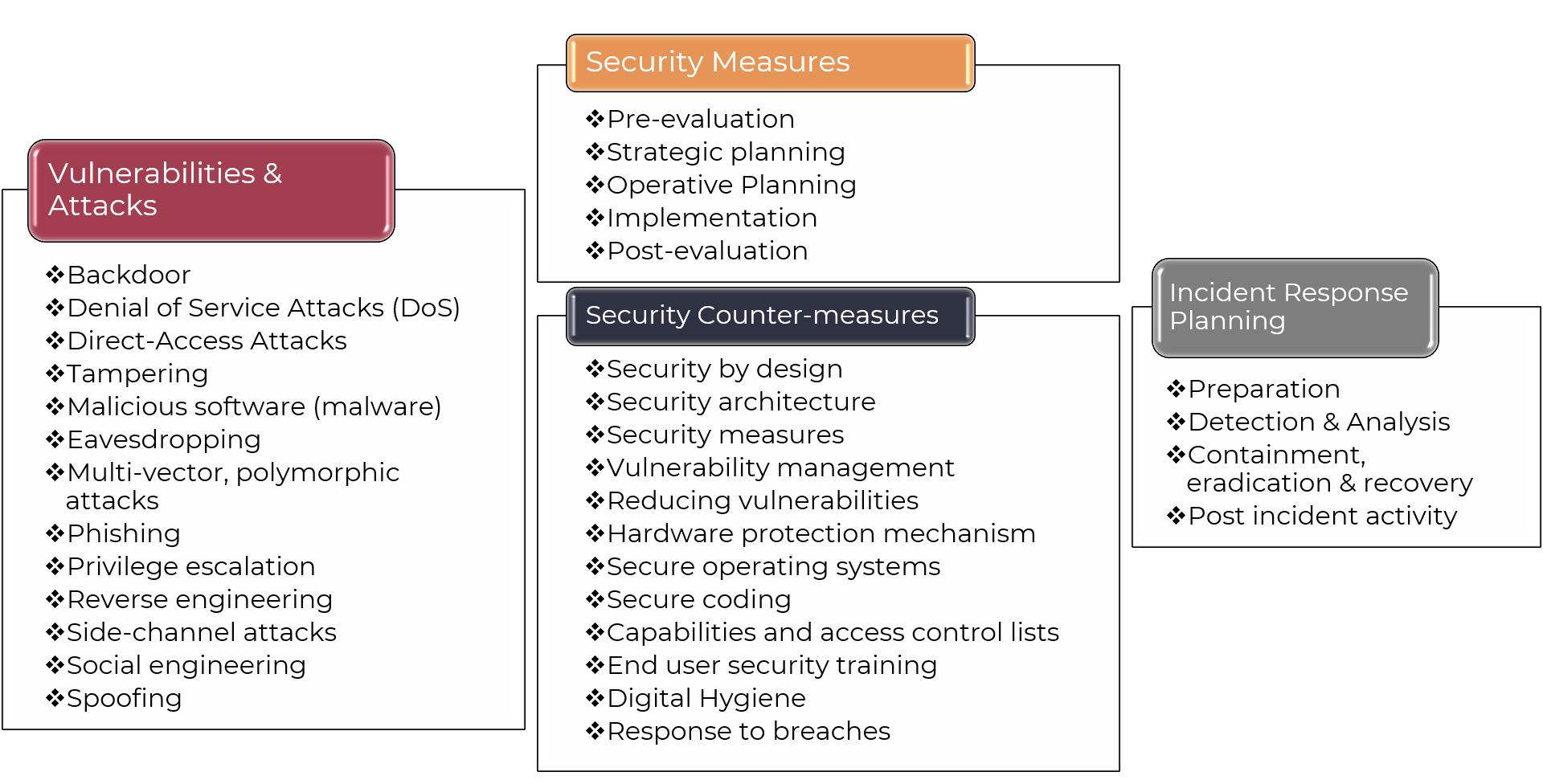
Vulnerabilities & Attacks
- Backdoor: A type of malware that allows unauthorized access to a computer system or network.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: A type of cyber attack where an attacker attempts to make a computer resource unavailable by overwhelming it with traffic.
- Direct-Access Attacks: A type of cyber attack where an attacker gains direct access to a computer system or network without authentication.
- Tampering: The act of modifying or altering data without authorization, often for malicious purposes.
- Malicious Software (Malware): Any software that is designed to cause harm or damage to a computer system or network.
- Eavesdropping: The act of intercepting and monitoring communications between two parties without their consent.
- Multi-vector, Polymorphic Attacks: A type of cyber attack where an attacker uses multiple vectors (e.g., email, social media) and creates multiple variants of malware to evade detection.
- Phishing: A type of social engineering attack where an attacker sends fraudulent emails or messages that appear to be from a legitimate source in order to trick victims into divulging sensitive information.
- Privilege Escalation: The act of gaining elevated access rights on a computer system or network without authorization.
- Reverse Engineering: The process of analyzing and understanding the functionality of software by disassembling it back into its original code.
- Side-channel Attacks: A type of cyber attack where an attacker exploits information that is not intended to be accessible, such as timing or power consumption data.
- Social Engineering: The act of manipulating individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing certain actions that compromise security.
- Spoofing: The act of disguising a message or communication to make it appear as though it comes from a trusted source.
Security Measures
- Pre-evaluation: A type of security measure where an organization assesses its current security posture and identifies areas for improvement.
- Strategic Planning: A type of security measure where an organization develops a comprehensive plan to address potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Operative Planning: A type of security measure where an organization implements specific strategies and tactics to prevent or respond to cyber attacks.
- Implementation: The process of putting security measures into place, such as installing software or hardware solutions.
- Post-evaluation: It is a crucial component of the security measure process, involving reviewing and assessing the effectiveness of implemented security measures to ensure they meet their intended goals and objectives.
Security Counter Measures
- Security by Design: A type of security countermeasure where an organization incorporates security considerations into the design and development phase of a system or application.
- Security Architecture: A type of security countermeasure where an organization designs and implements a secure architecture for its systems and applications.
- Vulnerability Management: A type of security countermeasure where an organization identifies, prioritizes, and remediates vulnerabilities in its systems and applications.
- Reducing Vulnerabilities: A type of security countermeasure where an organization takes steps to reduce the number of vulnerabilities in its systems and applications.
- Hardware Protection: A type of security countermeasure where an organization uses hardware solutions such as firewalls or intrusion detection systems to protect against cyber attacks.
- Secure Coding Practices: A type of security countermeasure where an organization follows secure coding practices, such as using secure protocols and encrypting sensitive data.
- Capabilities & Access Control Lists: This refers to the ability of an organization to define and manage access controls for its systems and data. Access control lists (ACLs) are used to grant or deny access to specific resources based on user identity, role, or other criteria.
- End User Security Training: This involves educating end-users about security best practices, such as how to identify and avoid phishing attacks, use strong passwords, and report suspicious activity. End-user training is critical in preventing human error from becoming a vulnerability.
- Digital Hygiene: Digital hygiene refers to the practices that individuals and organizations can follow to maintain good digital health. This includes keeping software up-to-date, using antivirus software, avoiding suspicious links or attachments, and regularly backing up data.
- Response to Breaches: A breach response plan outlines the procedures for responding to a security incident, including containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident activities.
Incident Response Planning
- Preparation: It involves developing and implementing plans, procedures, and protocols to respond effectively to potential incidents or breaches. This includes creating an incident response plan, conducting risk assessments, establishing communication protocols, identifying incident response teams, and developing incident response procedures to ensure timely and effective response to minimize downtime, damage, and reputational harm.
- Detection & Analysis: The process of detecting and analyzing a potential incident in order to determine the severity and impact.
- Containment, Eradication & Recovery: The process of containing the incident, eradicating the threat, and recovering from the incident.
- Post-incident Activity: The activities that take place after an incident has been resolved, including lessons learned and continuous improvement.
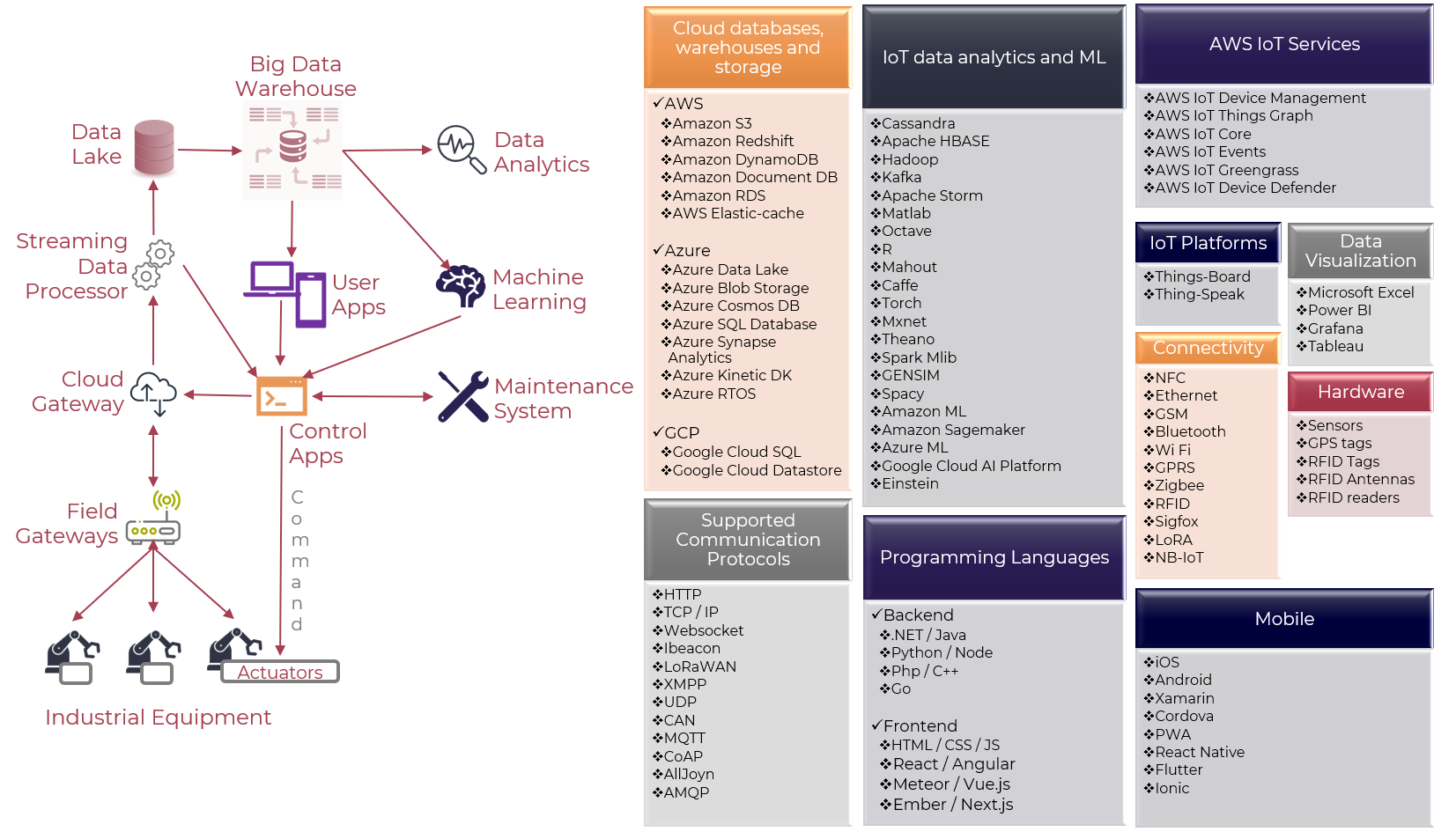
IIOT
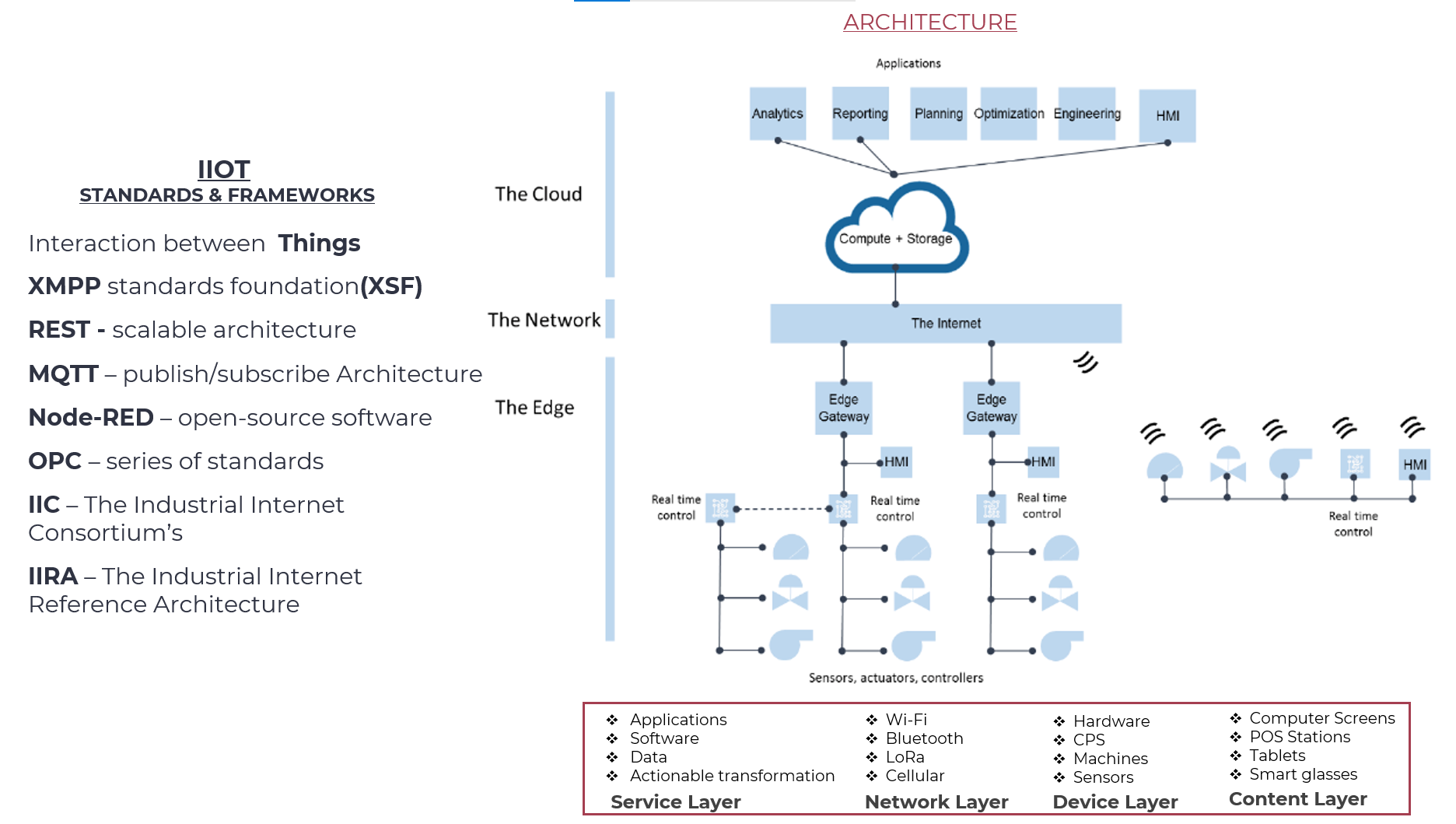
IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) is a technology that connects various devices, machines, sensors, and systems to the internet for real-time monitoring, control, and automation. It enables the collection and analysis of large amounts of data from industrial processes, equipment, and assets.
Standards and Frameworks:
The following are some key standards and frameworks used in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT):
- XMPP (Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol)
- XMPP is a standardized protocol for real-time communication over IP networks. It allows devices to communicate with each other through XML-based messages.
- REST (Representational State Transfer)
- REST is an architectural style that defines how applications interact with each other using HTTP protocols. It enables the creation of scalable and flexible APIs for data exchange.
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
- MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol designed for low-bandwidth, high-latency networks. It is widely used in IoT applications where devices need to send small amounts of data over long distances.
- Node-RED
- Node-RED is a visual programming tool that allows users to create complex workflows by connecting nodes and wires. It provides an intuitive interface for building IIoT applications without requiring extensive coding knowledge.
- OPC (Open Platform Communications)
- OPC is a set of industrial communication protocols used for data exchange between devices, systems, and applications. It enables real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes.
- IIC (Industrial Internet Consortium)
- IIC is an open forum that promotes the development and adoption of IIoT technologies. It provides a platform for collaboration among industry leaders to create standards and best practices for IIoT implementation.
- IIRA (International Industrial Reference Architecture)
- IIRA is an architectural framework for designing and implementing industrial automation systems. It provides guidelines for integrating devices, sensors, and equipment with IT systems using open standards.
Architecture:
The IIoT architecture consists of four layers:
- Device Layer: This layer includes the hardware components that interact with the physical environment, such as sensors, actuators, and controllers.
- Network Layer: This layer enables communication between devices using protocols like XMPP, REST, or MQTT.
- Service Layer: This layer provides services to devices, including data processing, analytics, and decision-making capabilities.
- Content Layer: This layer includes the data generated by devices, which is used for analysis, visualization, and other applications.
Simulation

Simulation Techniques
- Discrete Event Simulation (DES): This technique models complex systems by dividing them into discrete events or stages. It’s particularly useful for analyzing production lines and supply chains.
- System Dynamics (SD): SD focuses on the dynamic behavior of complex systems over time. It helps analyze how different variables interact within a system.
- Agent-Based Modeling (ABM): ABM simulates the behavior of individual agents or entities in a system. This technique is useful for modeling human decision-making and social interactions
- Intelligent Simulation: Intelligent simulation uses artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to simulate complex systems. It enables the analysis of dynamic behavior and adaptation to changing conditions.
- Petri-net: Petri-net is a visual representation of processes and their interactions. It helps model complex systems and analyze their behavior.
- Monte Carlo Simulation: Monte Carlo simulation uses random sampling to estimate probabilities and outcomes in complex systems. It’s particularly useful for analyzing risks and uncertainties.
- Virtual Simulation: Virtual simulation creates virtual environments that mimic real-world conditions. It allows for the testing and validation of new products, processes, and systems without physical prototypes.
- Hybrid Techniques: Hybrid techniques combine multiple simulation methods to analyze complex systems from different perspectives. They provide a more comprehensive understanding of system behavior and interactions
Digital Twin
-
A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical system or process, enabling real-time monitoring, prediction, and optimization. It provides a detailed model of the system’s behavior, allowing for simulation and analysis under various conditions.
-
Characteristics
- Digital Traces: Digital twins provide real-time data on production processes, enabling continuous monitoring and optimization.
- Modularity: Modular digital twins allow for easy integration with existing systems and flexibility to adapt to changing requirements.
- Connectivity: Connectivity enables seamless communication between different digital twin tools and models, facilitating the exchange of data and insights.
- Homogenisation: Homogenization ensures that all data is standardized, making it easier to analyze and compare results.
- Reprogrammable & Smart: Digital twins can be reprogrammed and optimized in real-time, enabling quick adaptation to changing conditions.
Horizontal and Vertical Integration
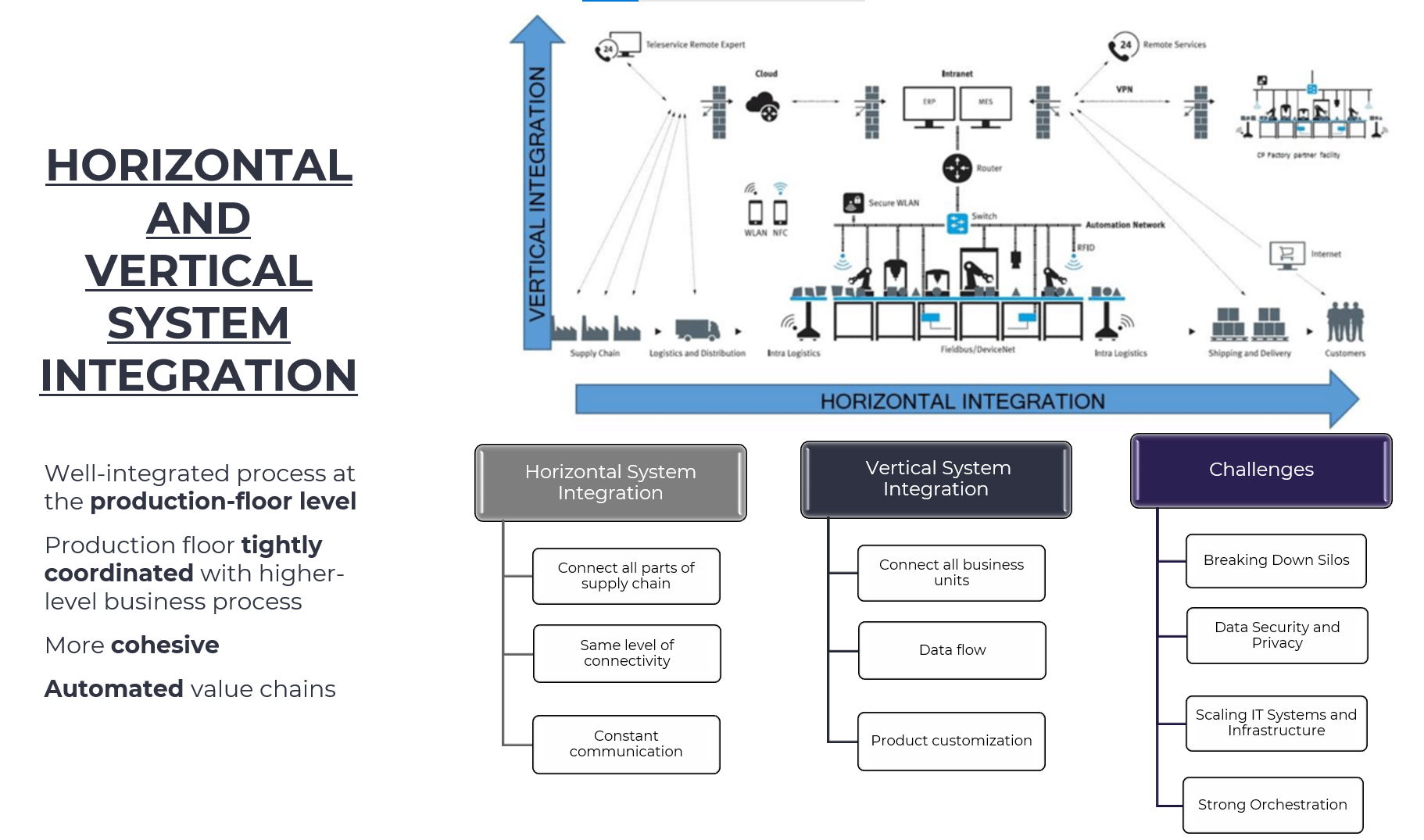
Horizontal System Integration
- Horizontal system integration refers to the process of connecting all parts of a supply chain together using technology.
- This approach aims to create a seamless flow of goods, services, and information from raw materials to end customers.
- Layers
- Supply Chain Management: Managing the flow of goods, services, and information from raw materials to end customers.
- Inventory Control: Ensuring that products are available at the right time and in the right quantities.
- Production Planning: Planning and scheduling production activities to meet customer demands.
- Benefits
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Streamlining processes, reducing costs, and increasing productivity.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Providing a seamless experience from ordering to delivery.
- Increased Competitiveness: Responding quickly to changing market conditions and customer demands.
- Challenges
- Technical Challenges: Integrating different systems and technologies can be complex.
- Organizational Challenges: Coordinating across departments and teams requires significant changes to organizational structures and processes.
- Data Integration Challenges: Integrating data from different sources can be challenging, especially if the data is not standardized or compatible.
Vertical System Integration
- Vertical system integration refers to the process of connecting different levels of an organization’s operations together using technology.
- This approach aims to create a cohesive and efficient operation by integrating various functions such as production, logistics, and customer service.
- Layers
- Integration of Functions: Integrating various functions such as production, logistics, and customer service to improve operational efficiency.
- Standardization of Processes: Standardizing processes across different departments and teams to reduce errors and increase productivity.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Analyzing data from different sources to provide insights for decision-making.
- Benefits
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Streamlining processes, reducing costs, and increasing productivity.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration across departments and teams to improve communication and reduce errors.
- Better Decision-Making: Providing insights for decision-making through data analysis and reporting.
- Challenges
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes to their roles or responsibilities, making it challenging to implement vertical system integration.
- Technical Challenges: Integrating different systems and technologies can be complex, especially if they are not compatible.
- Data Security Concerns: Integrating data from different sources can raise concerns about data security and privacy.
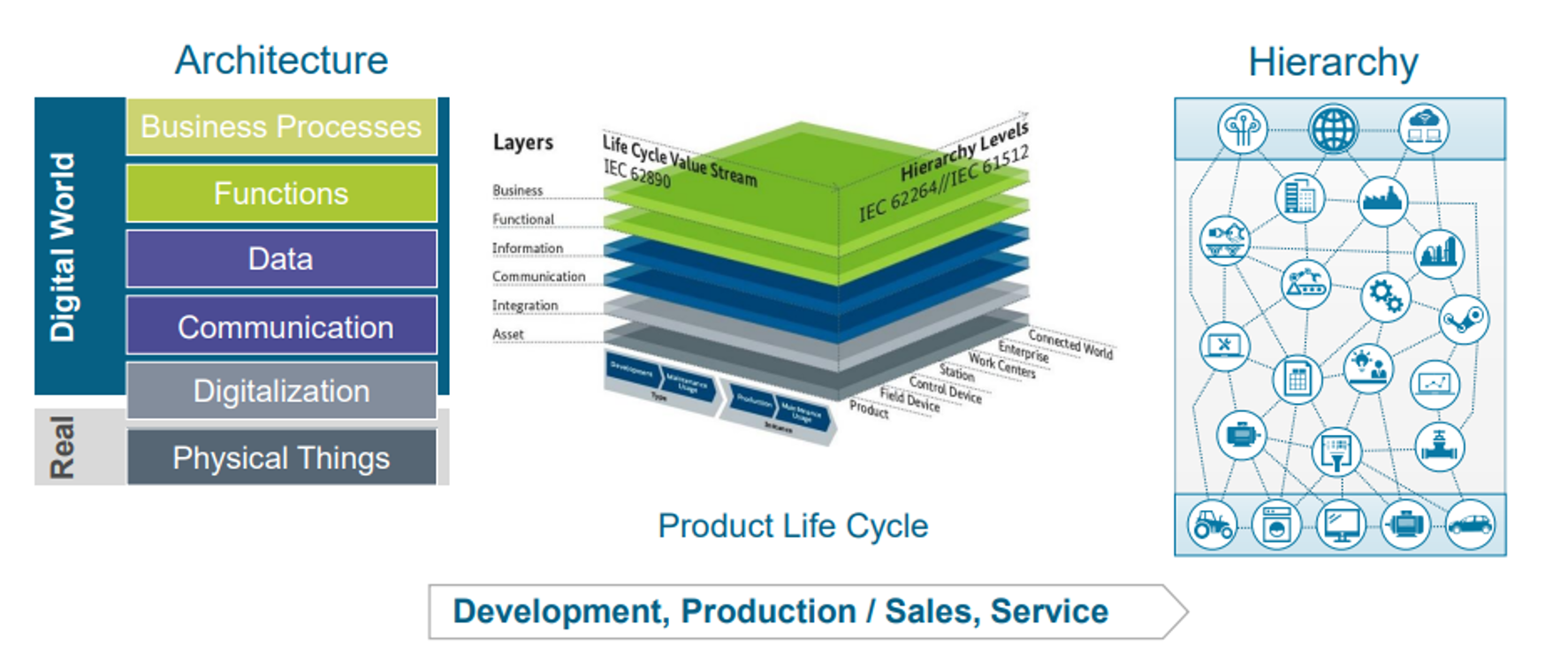
Reference Architectures
RAMI 4.0
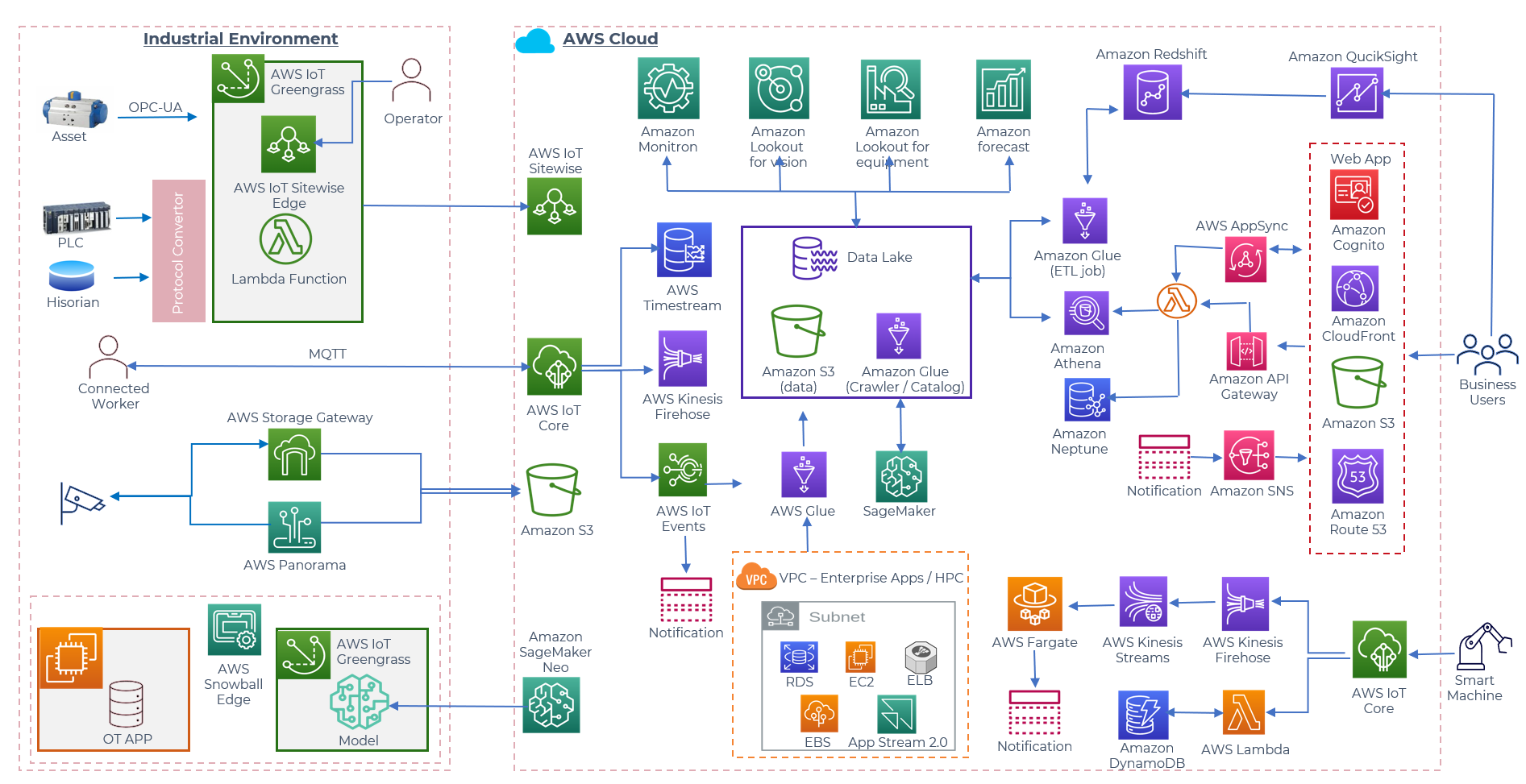
AWS Industrial
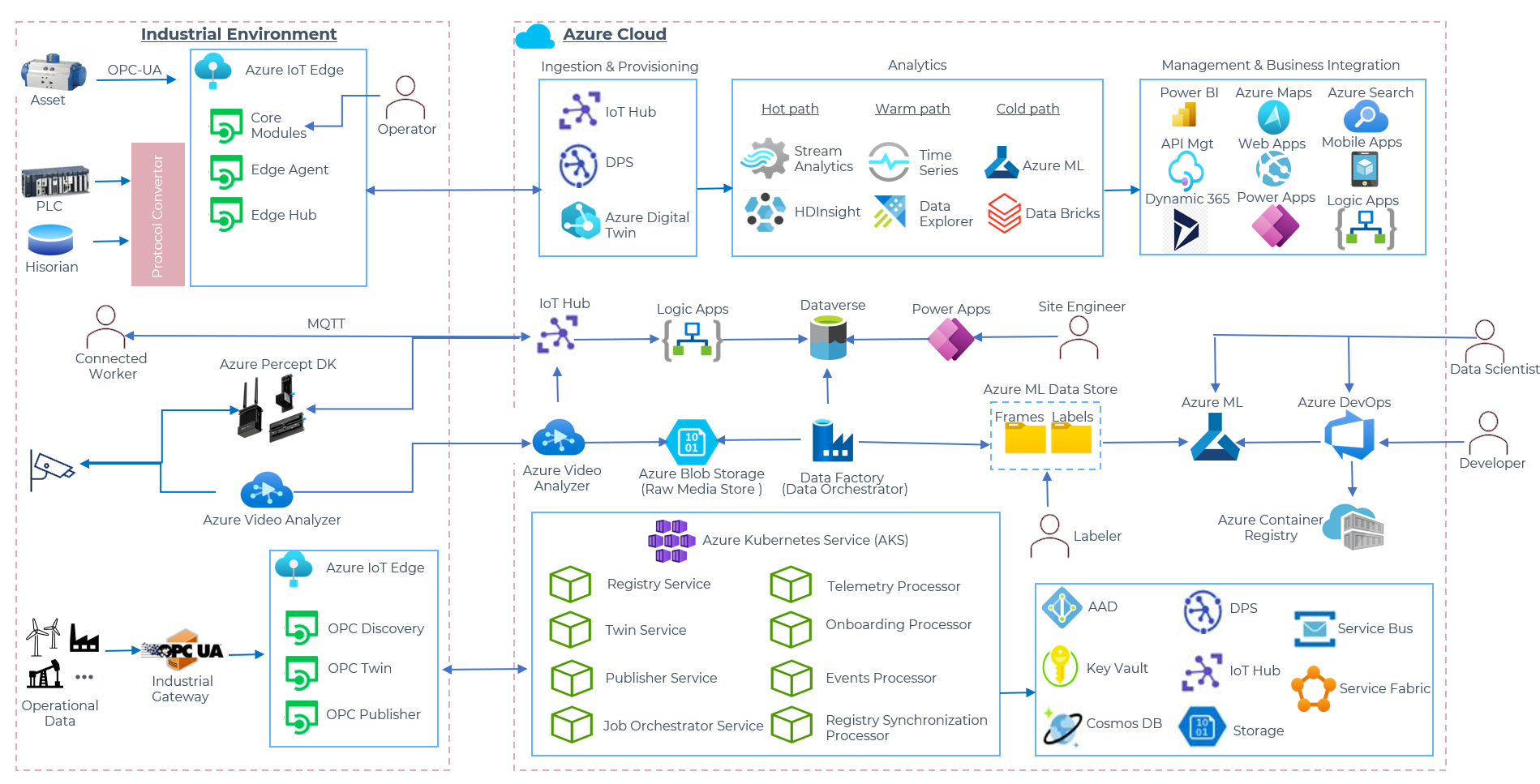
Azure Industrial
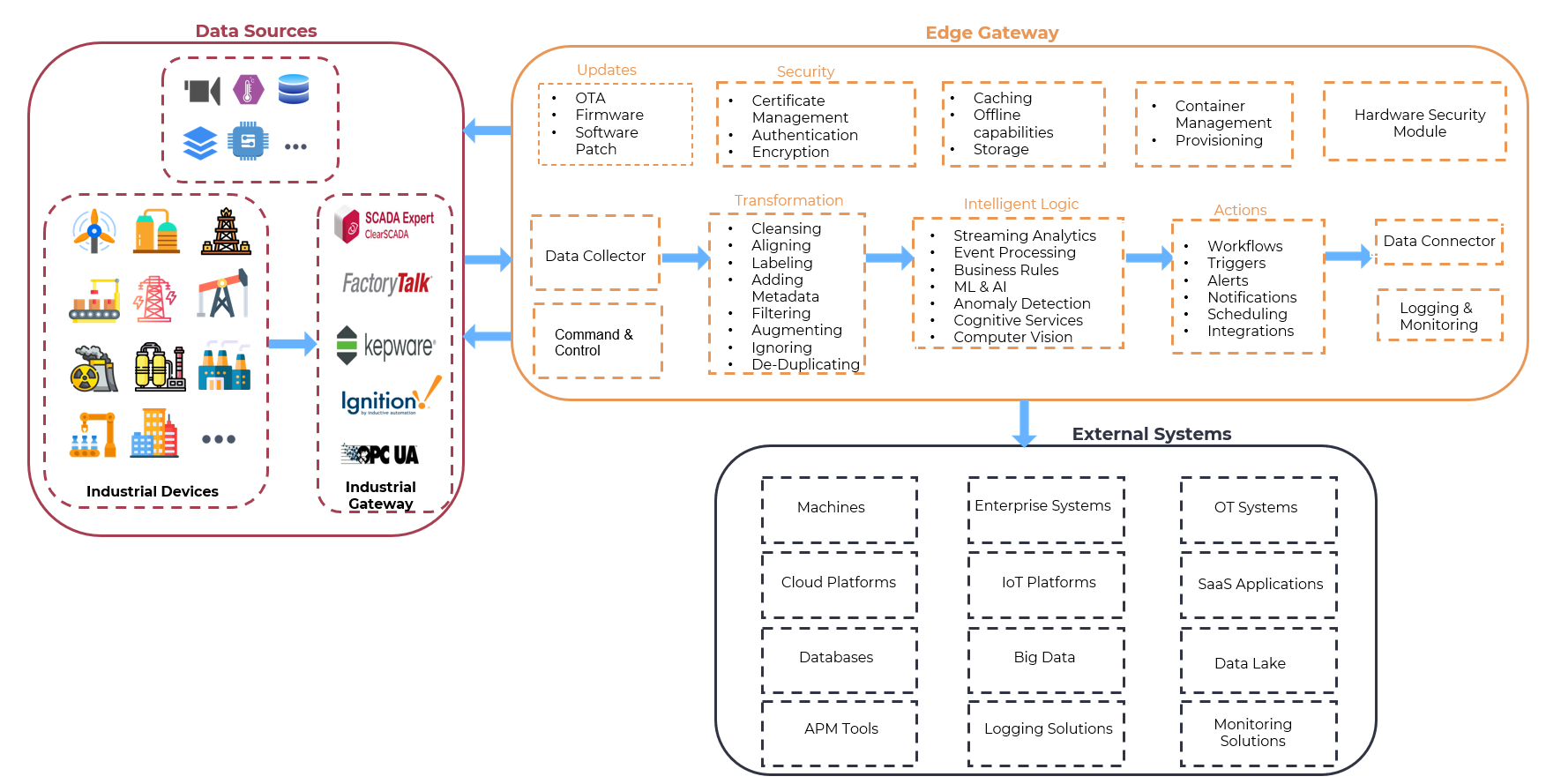
Edge Compute
Predictive Maintenance
Overall Equipment Effectiveness
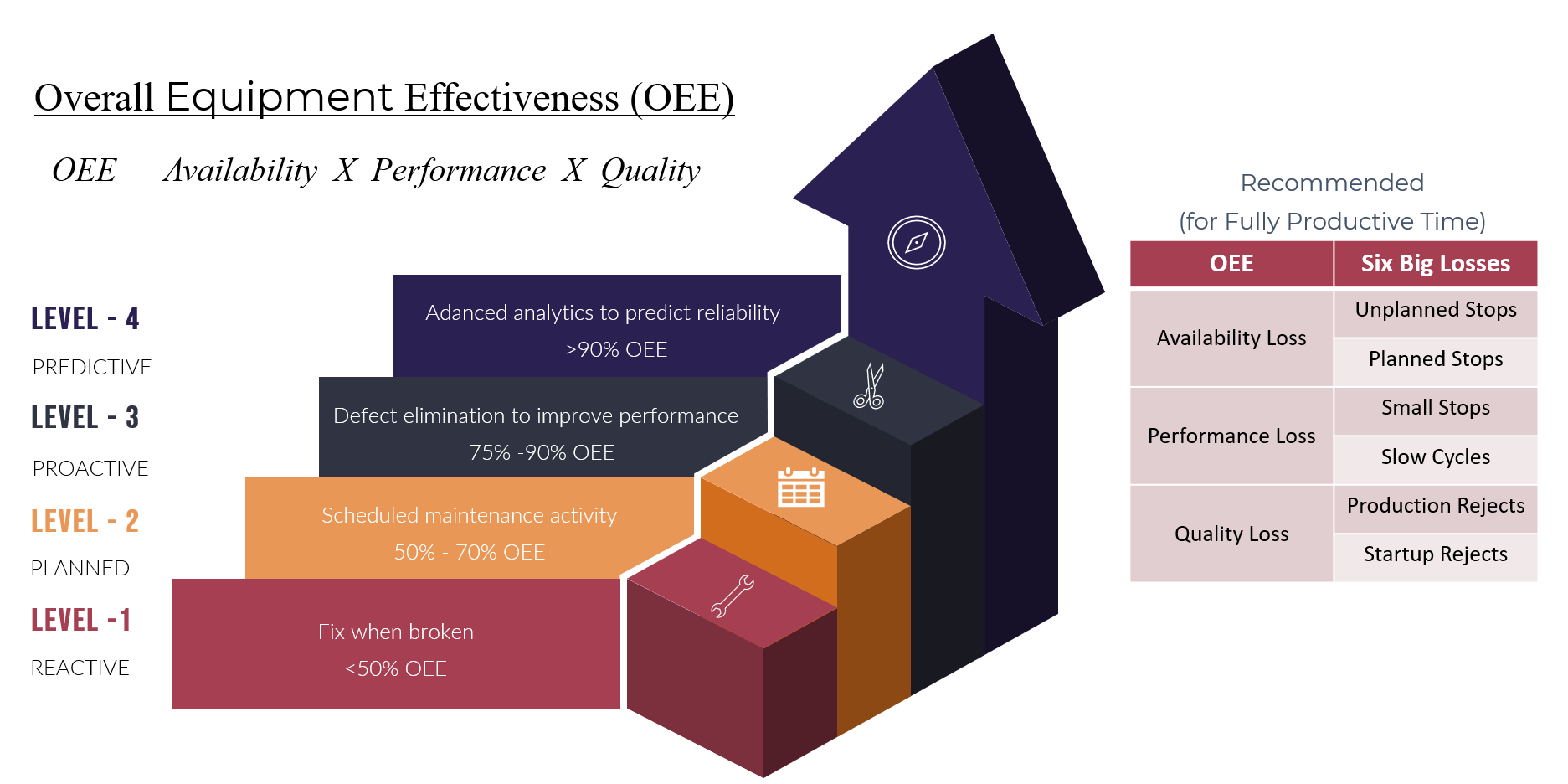
Plant Architecture
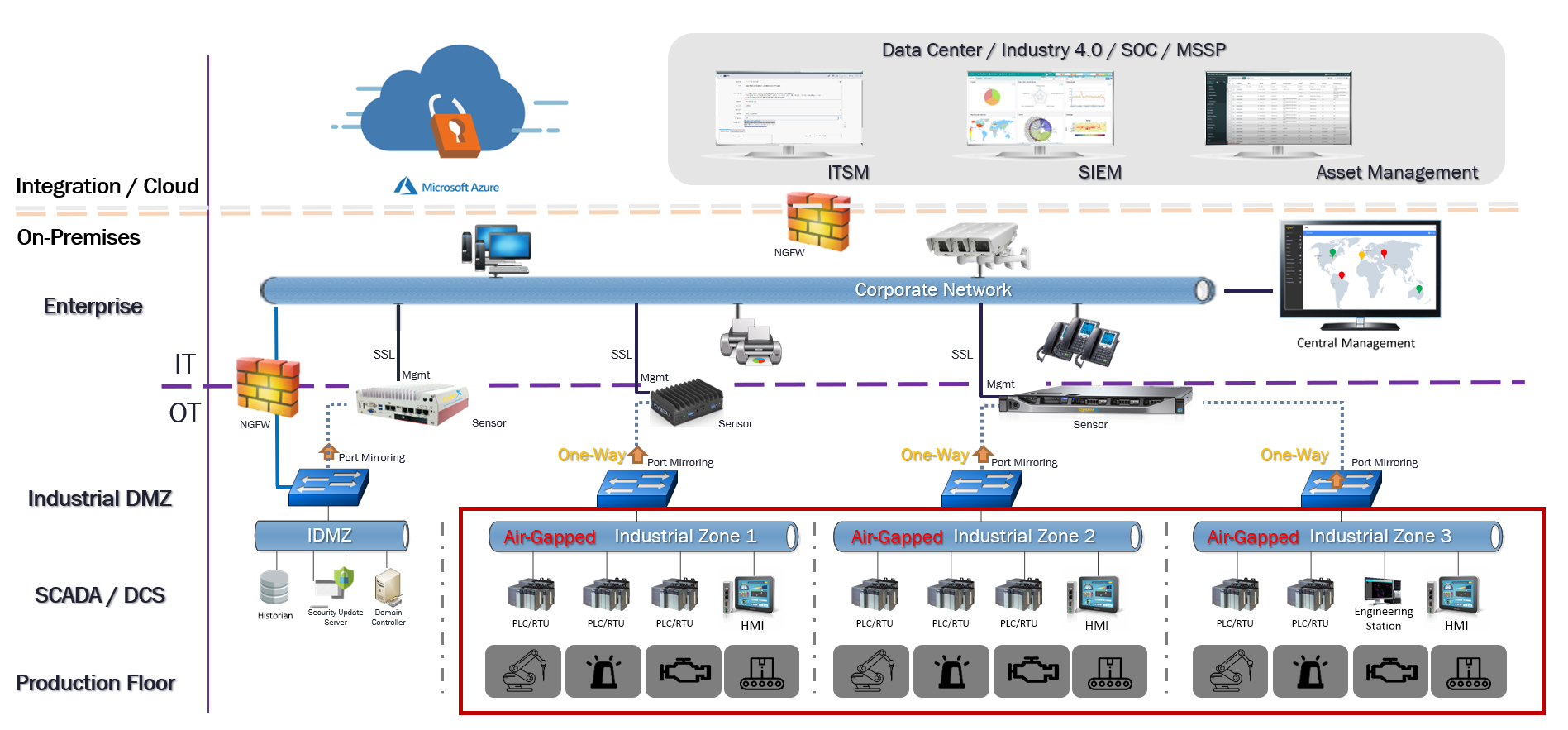
Industrial Control System Components

Workloads
Key Enablers
Digitalization Journey

Use cases
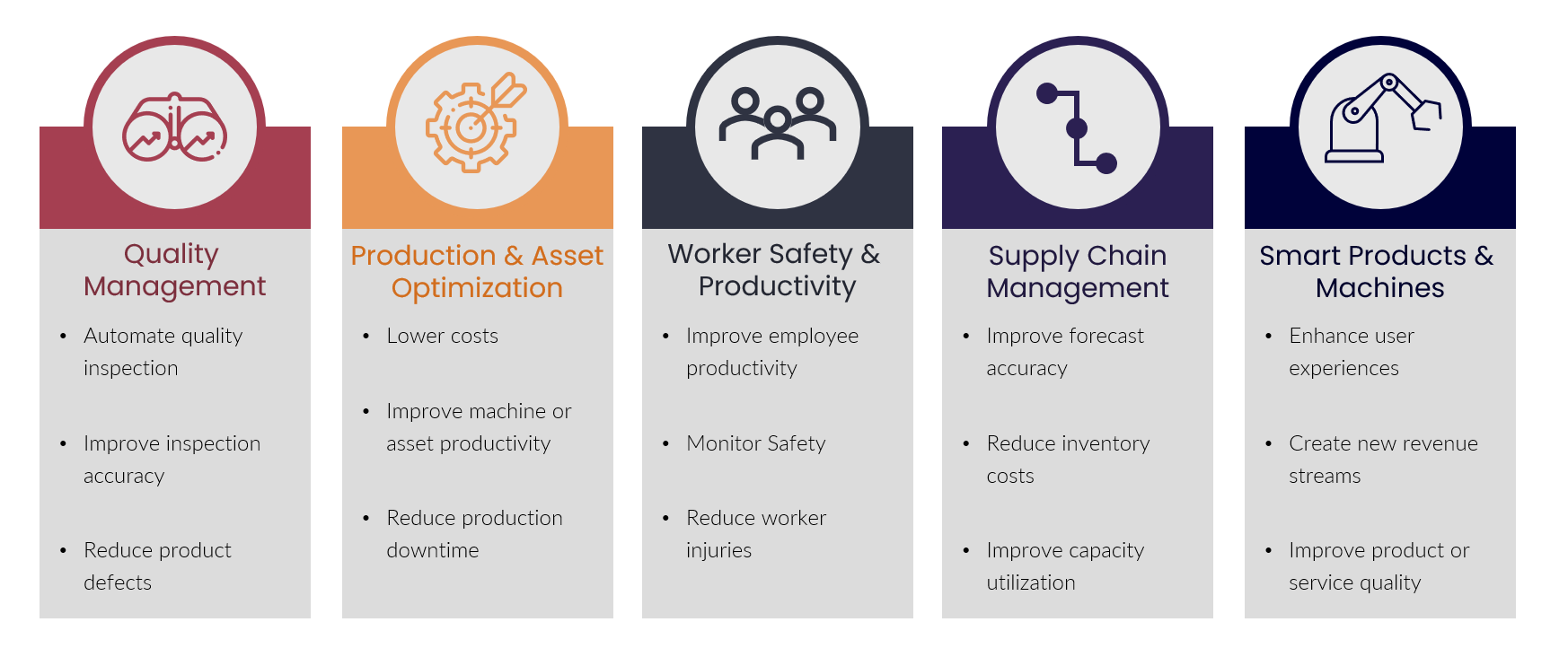
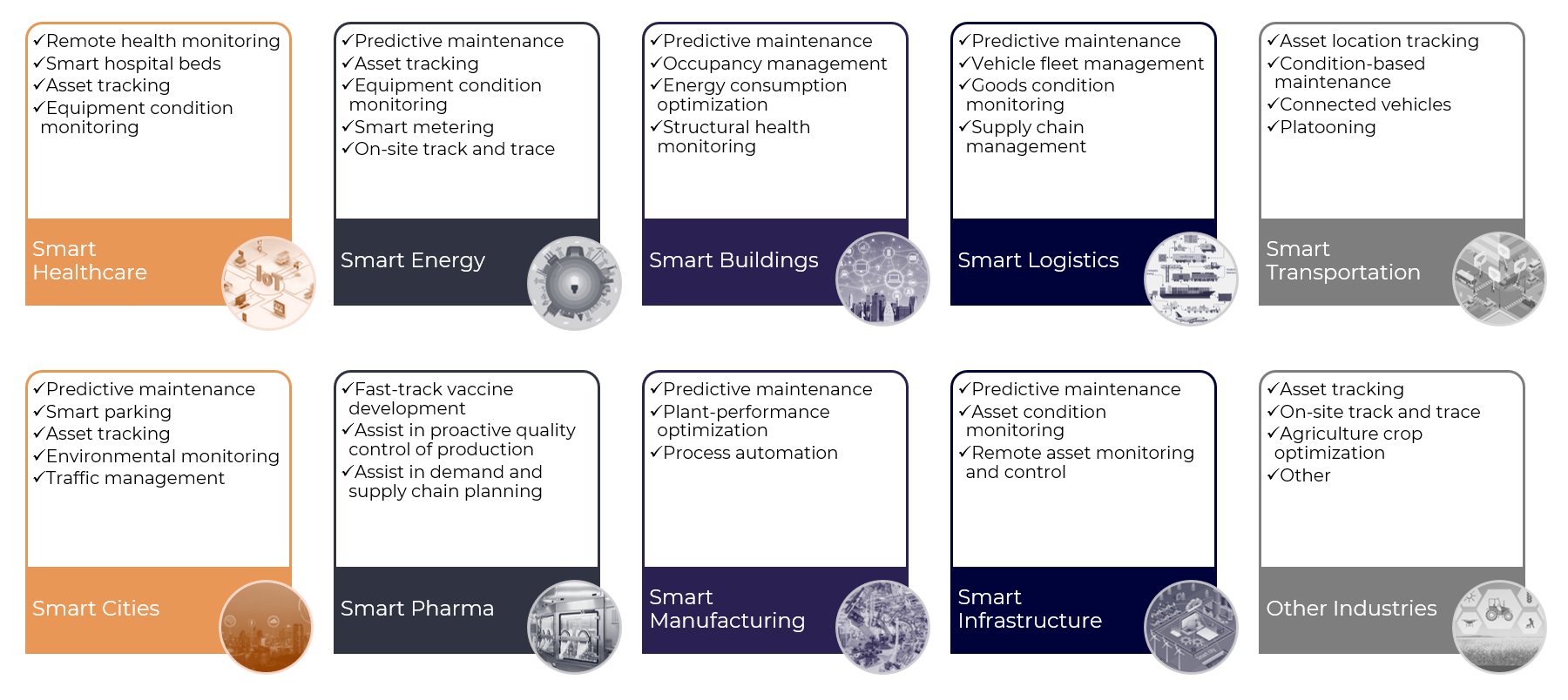
Capabilities
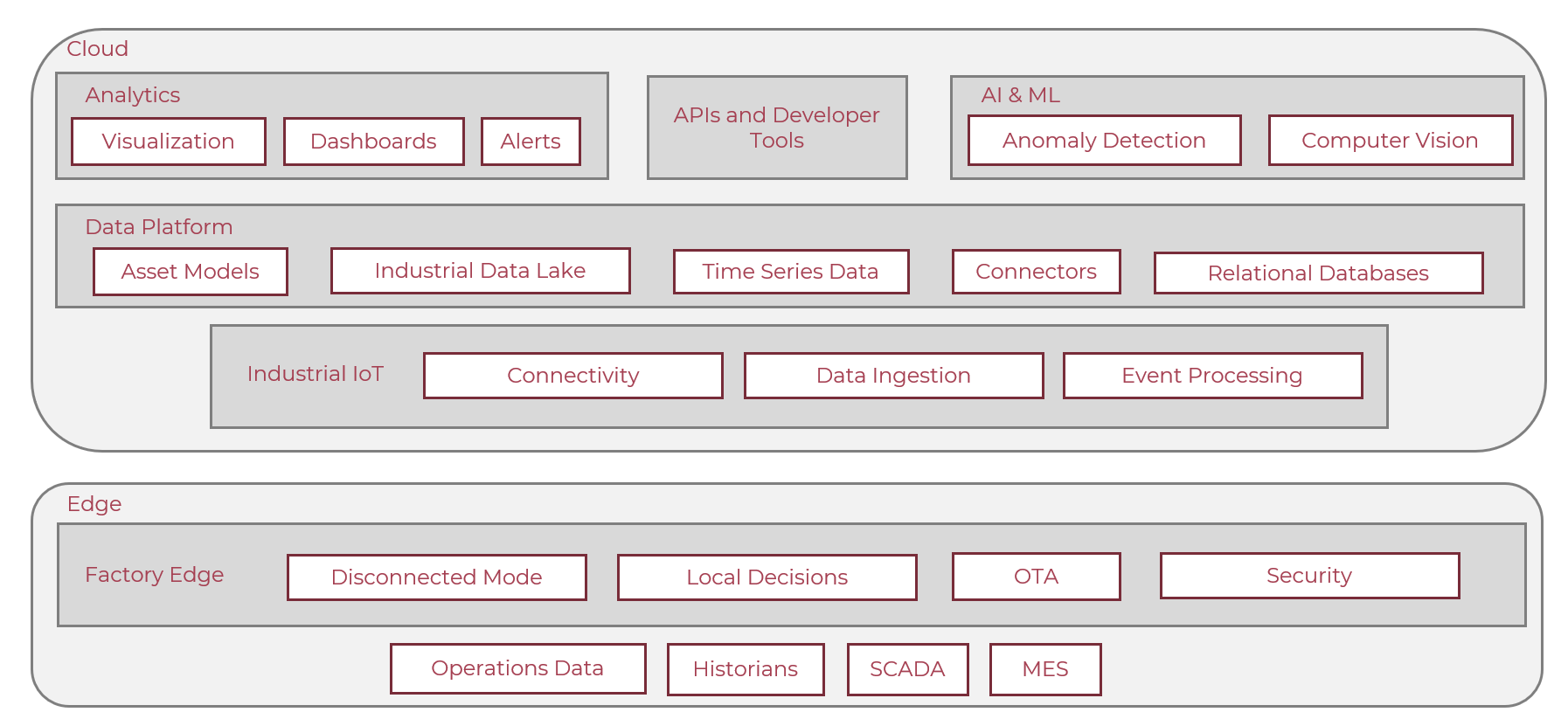
Demos
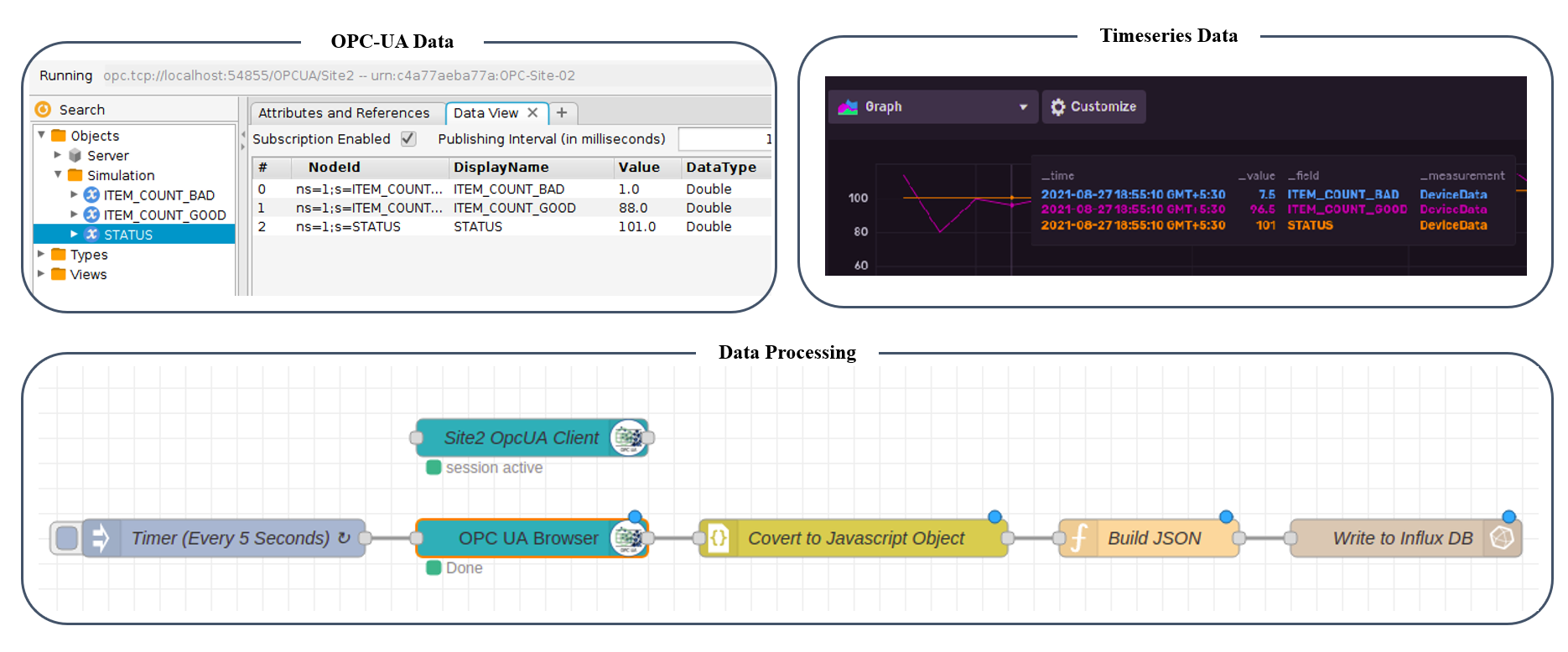
OPC-UA Pipeline (On-Premise)

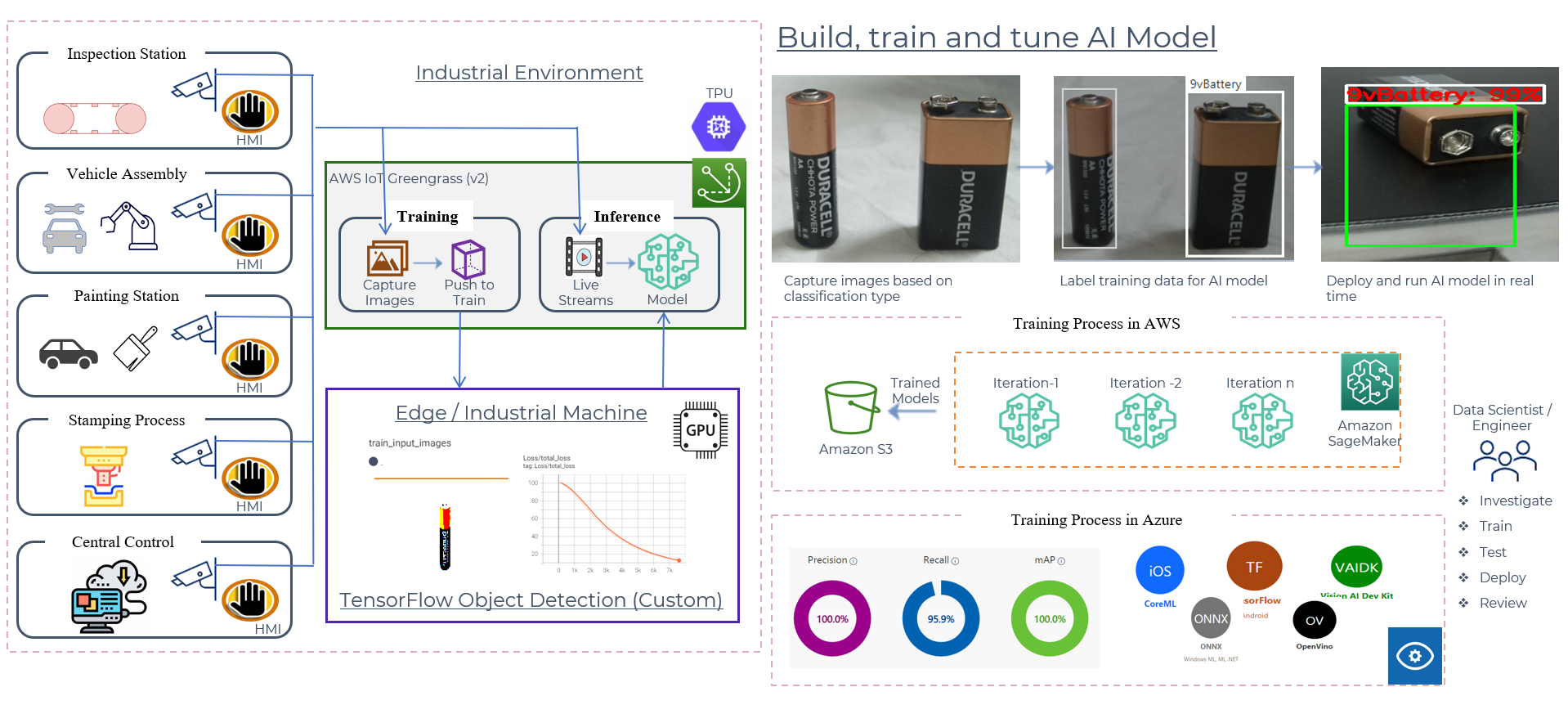
Computer Vision at the Edge
Virtual Andon
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_2Wfz4T_yP0
IT vs OT Security
Network Topologies in OT Environment
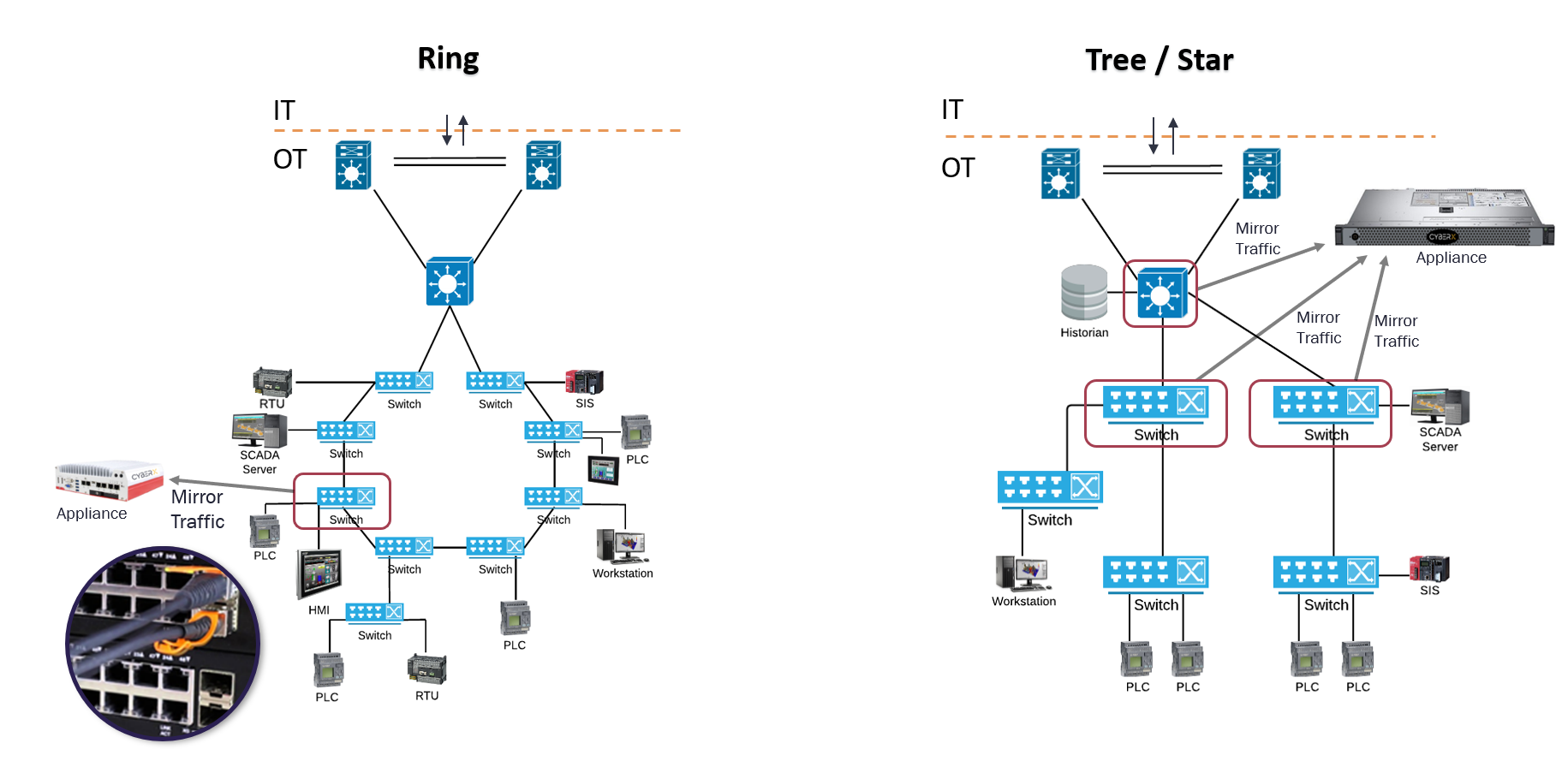
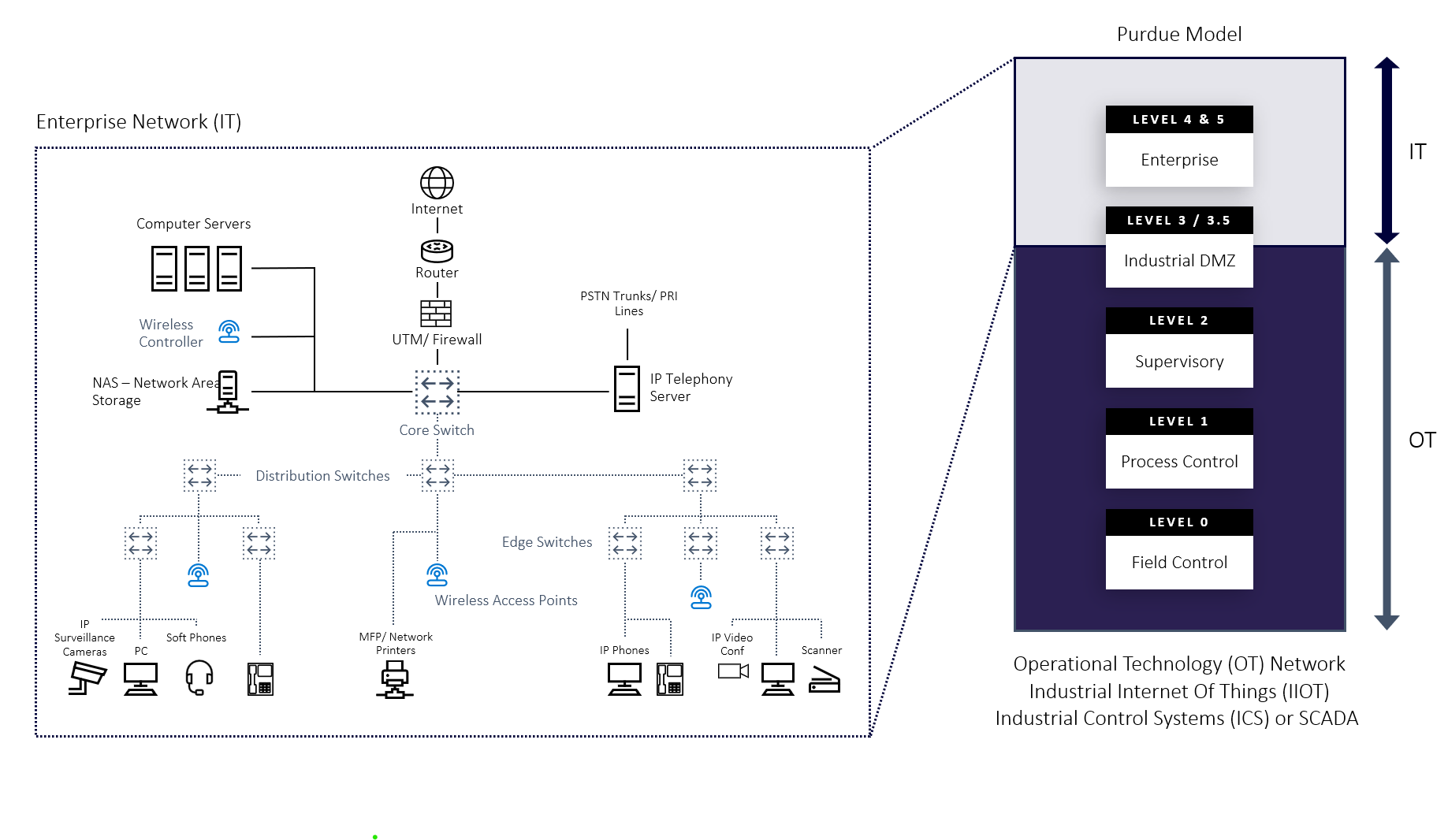
IT and OT Networking Background
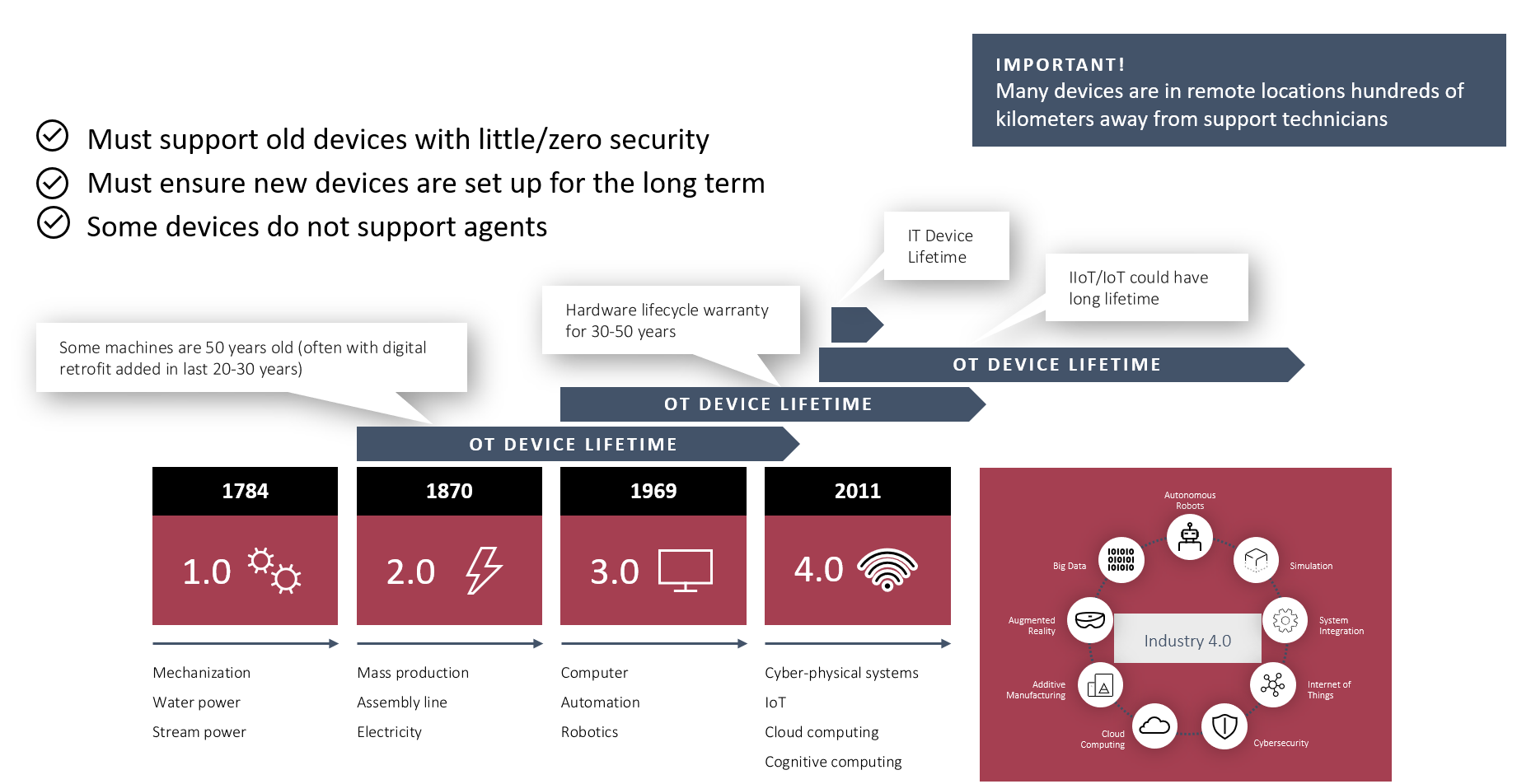
Challenges
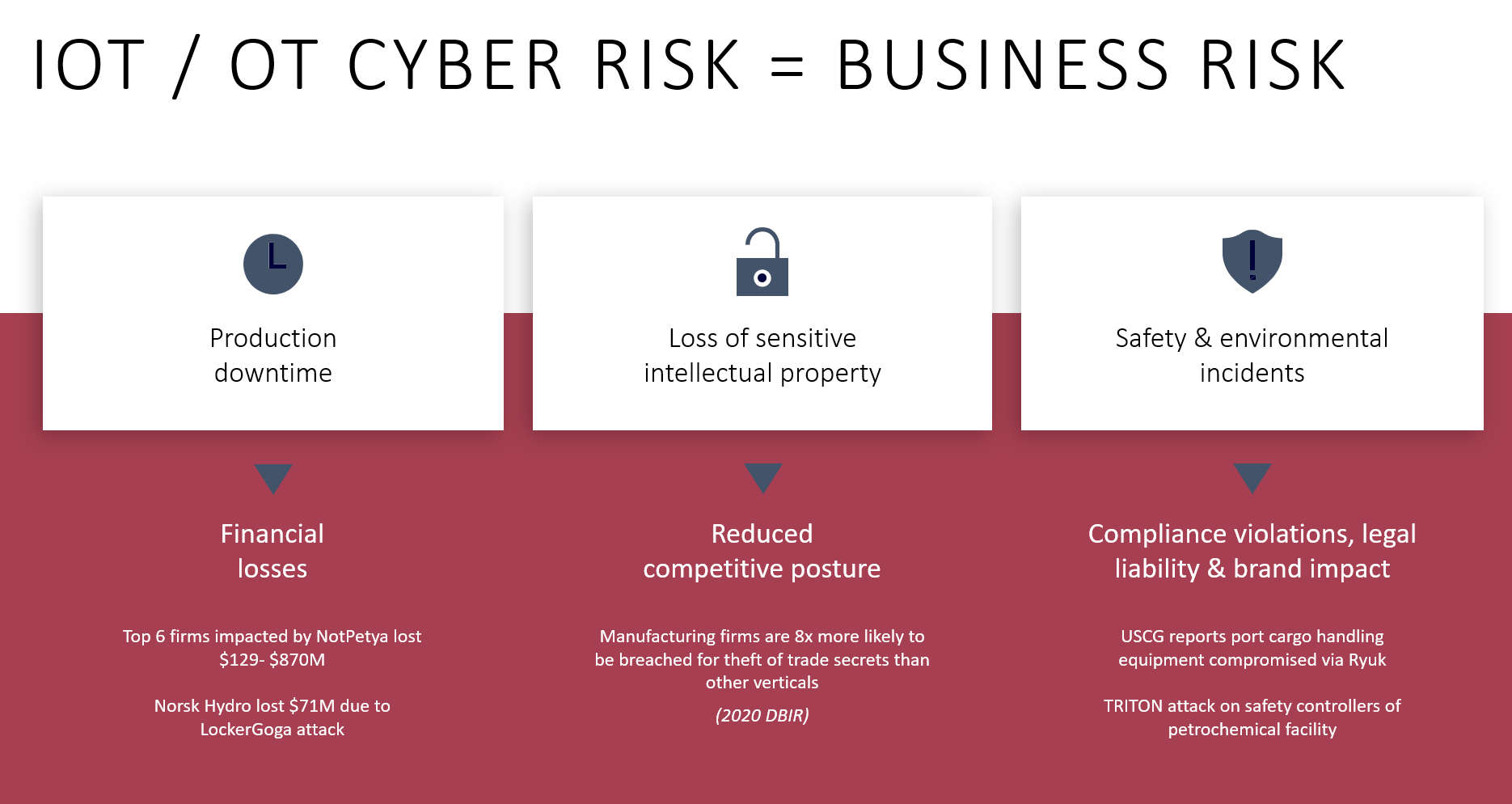
Business Risk
TRITON Attack
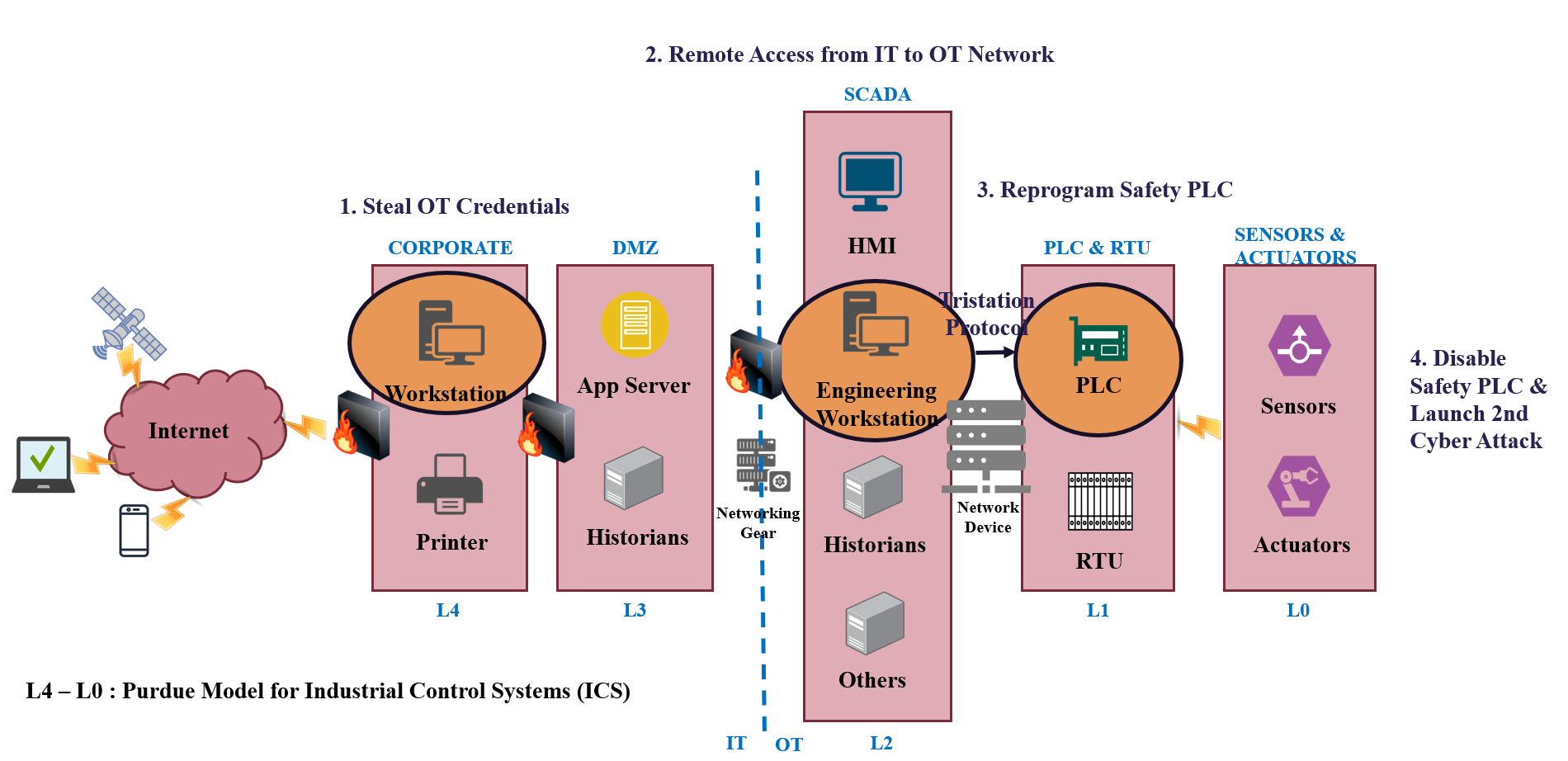
How Gartner Defines?

IT Security vs OT Security
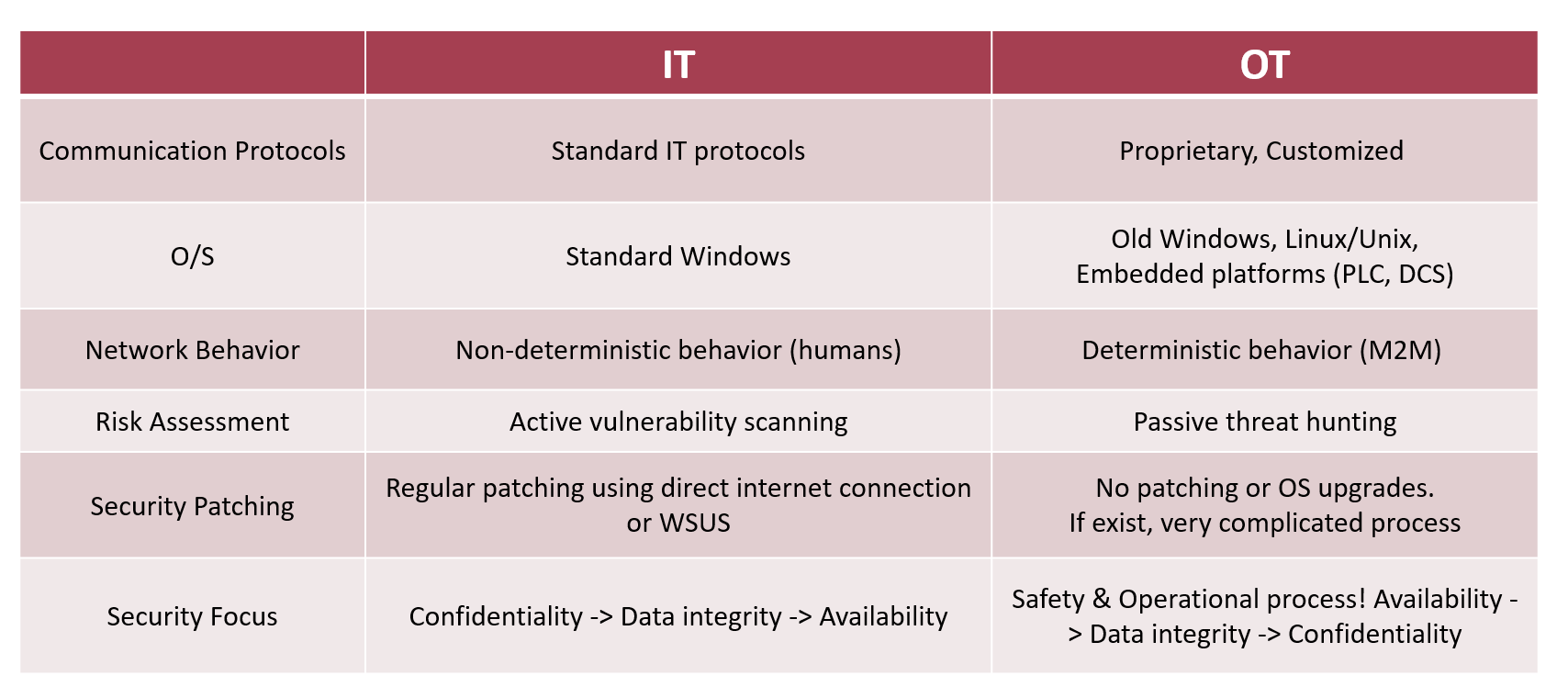
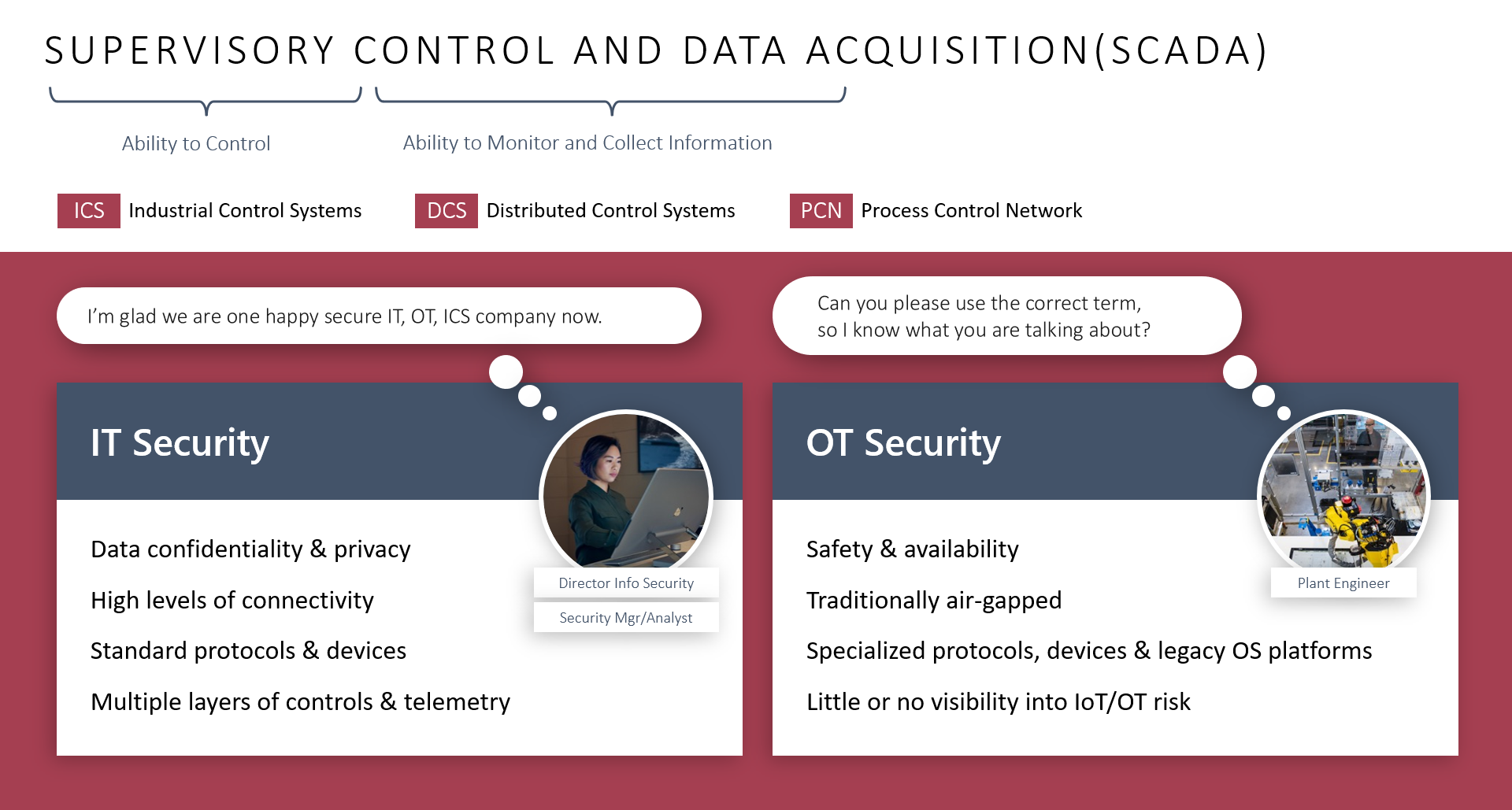
SCADA
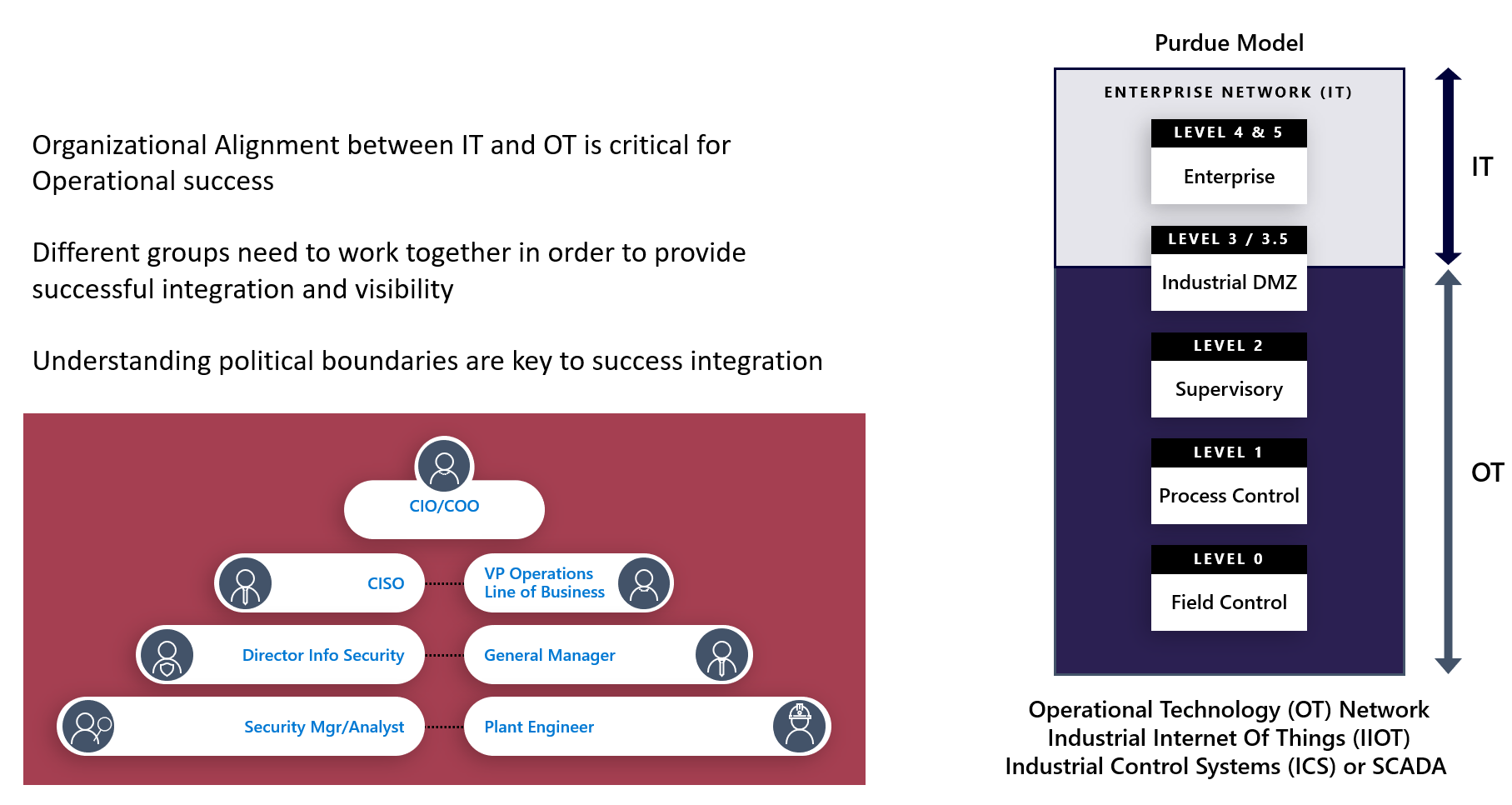
Aligning IT & OT
Events that Affect IoT / OT Networks
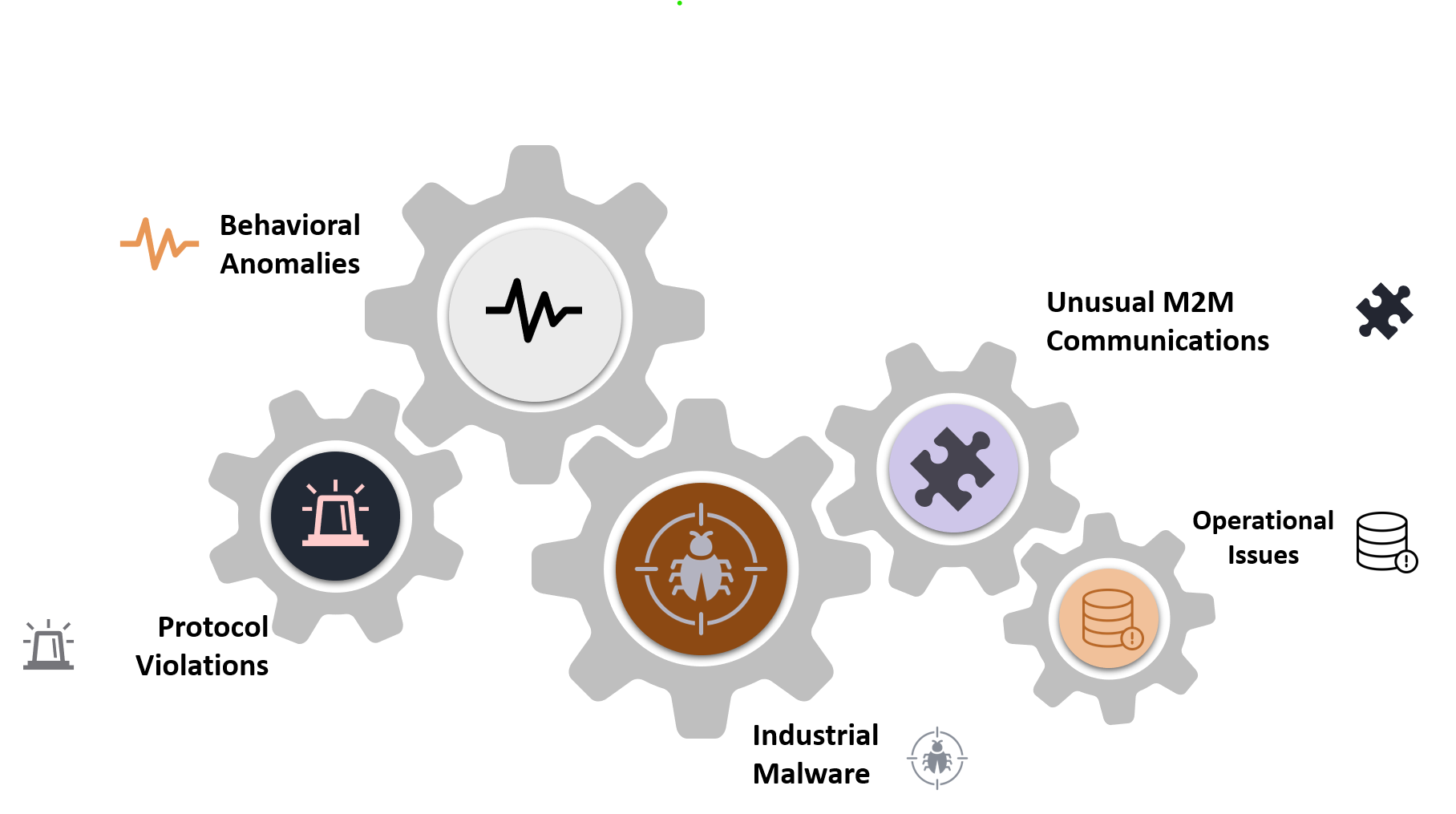
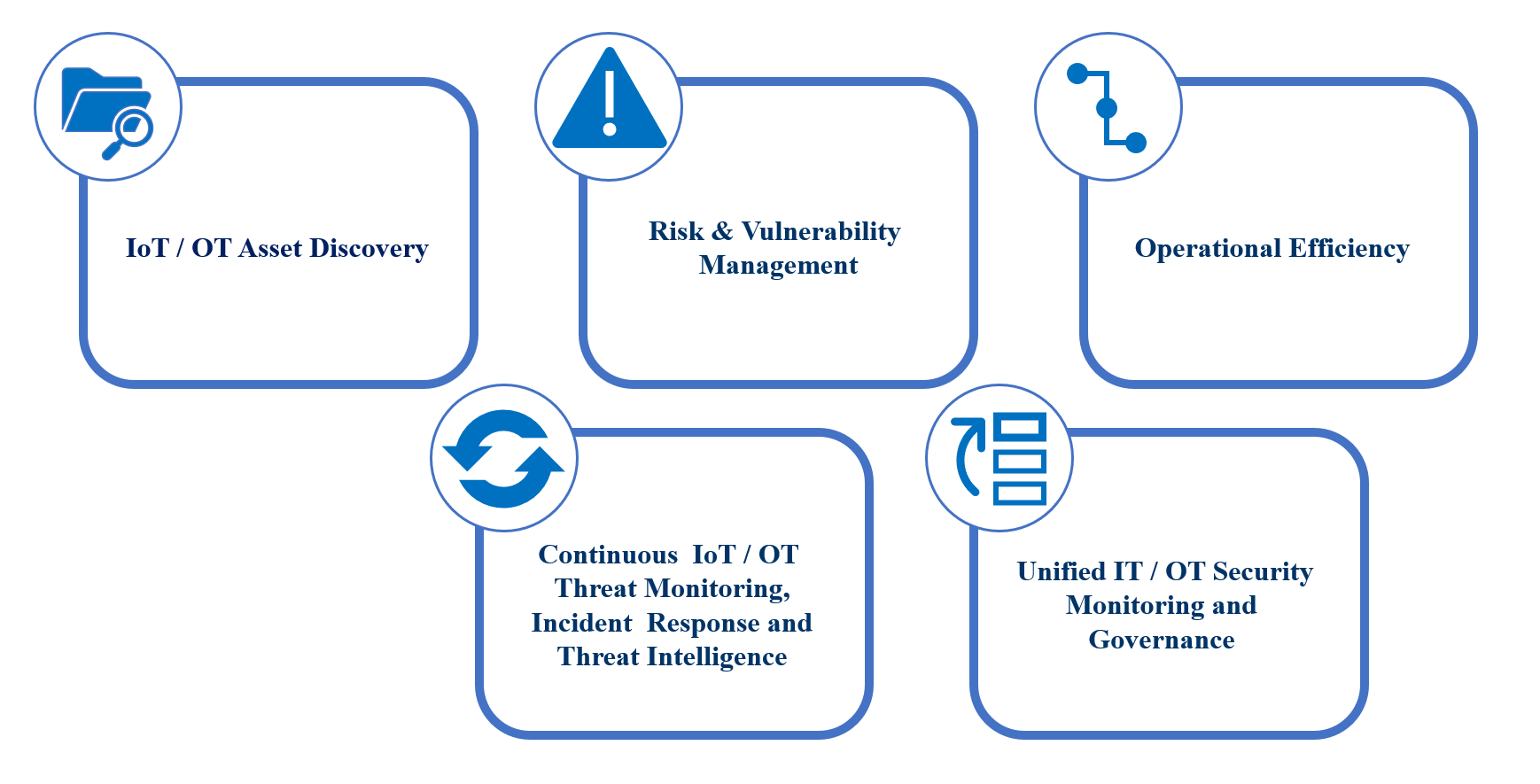
Microsoft Defender for IoT
Features
Reference Architecture
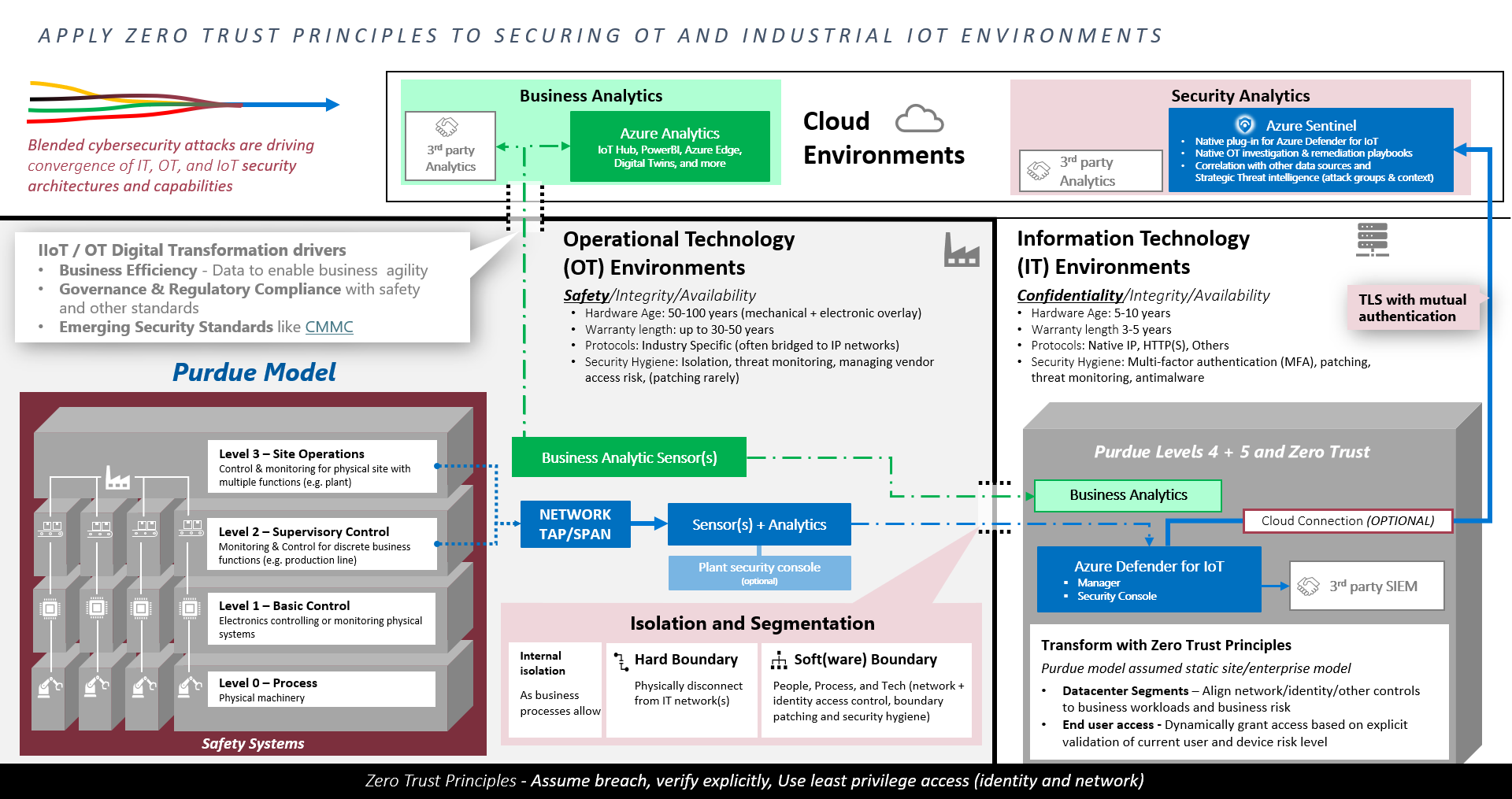
Unified, E2E Protection
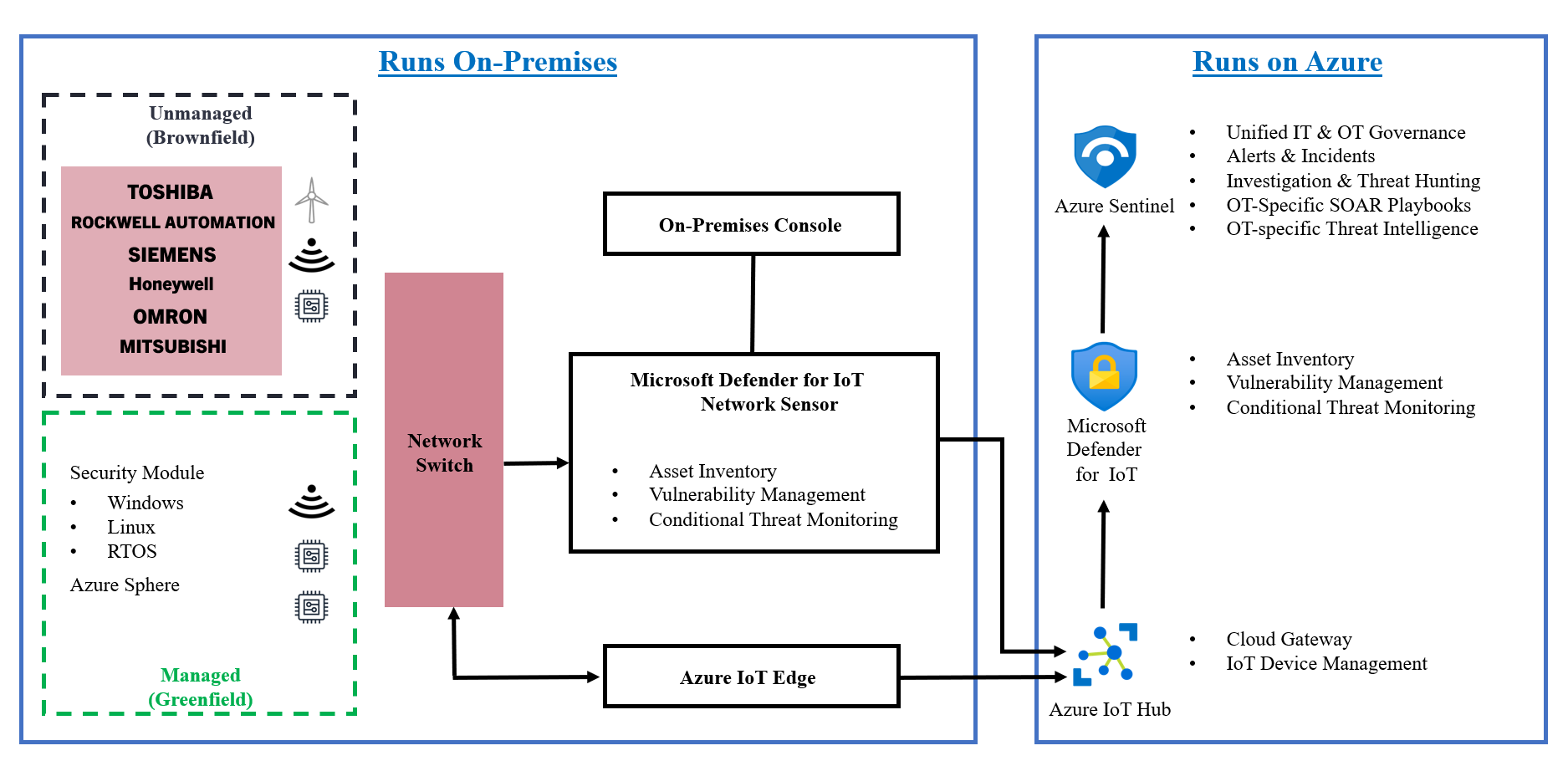
Deployment Options
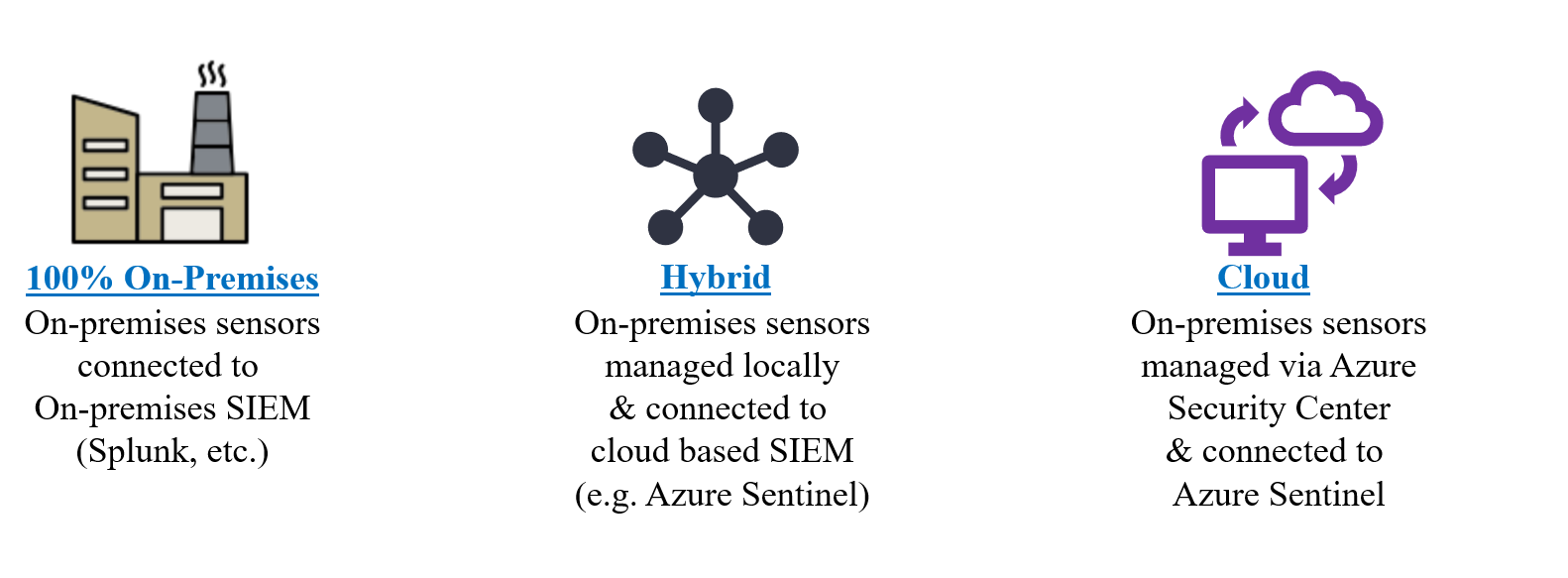
Recommended Deployment Process
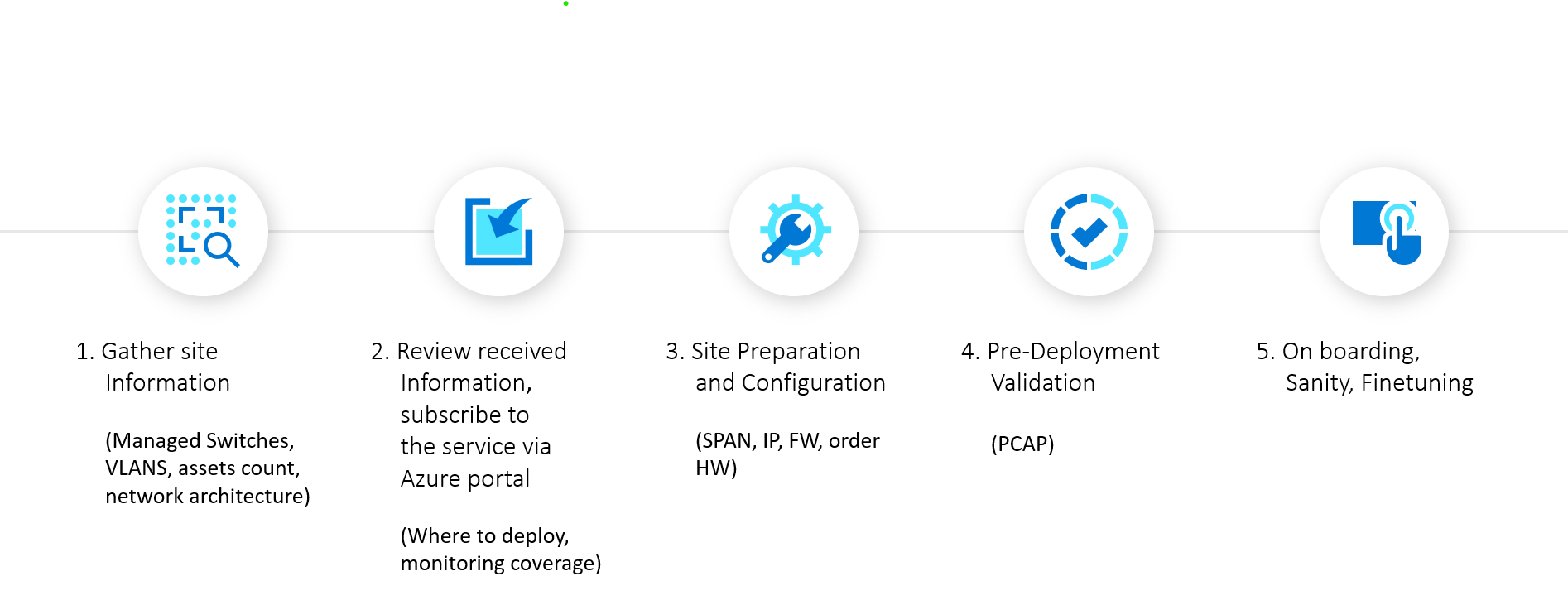
9 Steps Deployment Process
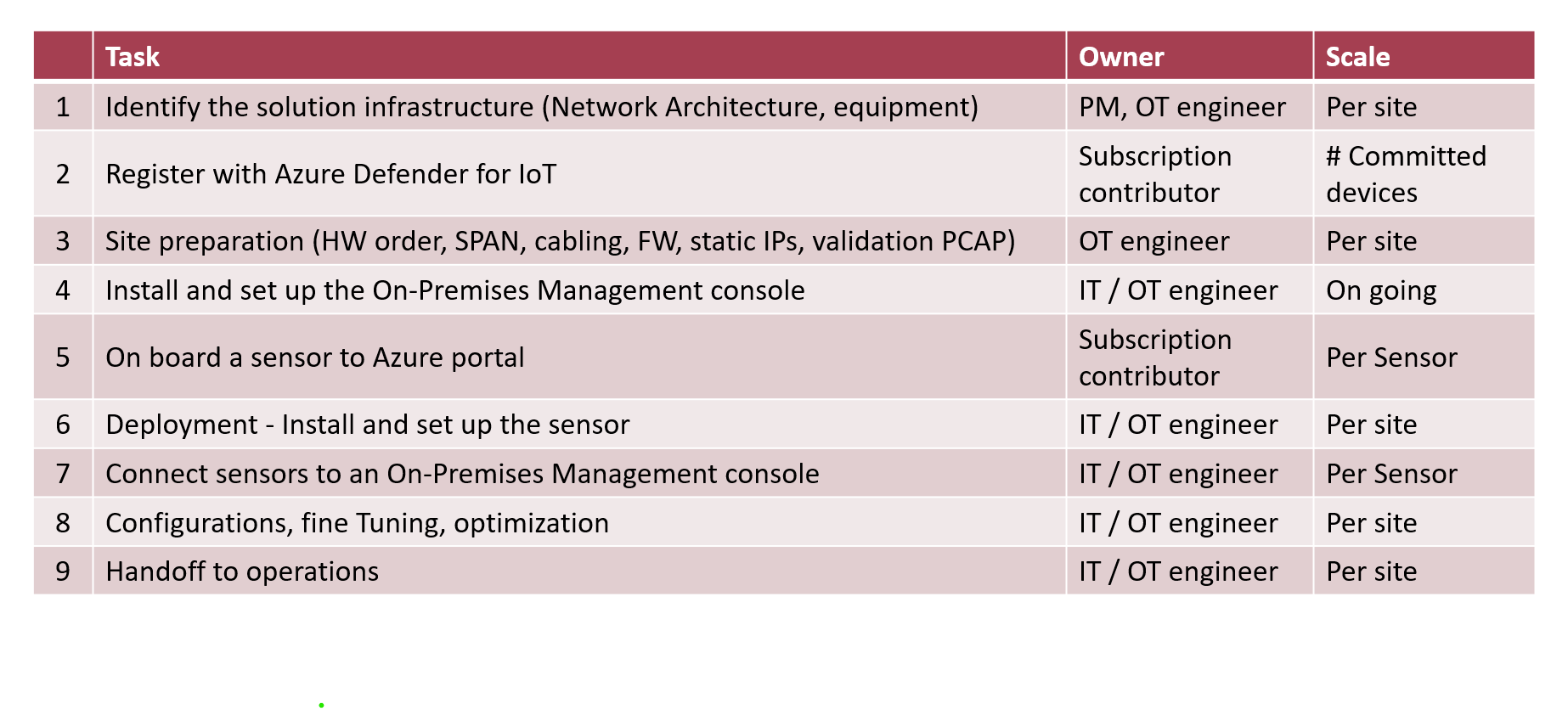
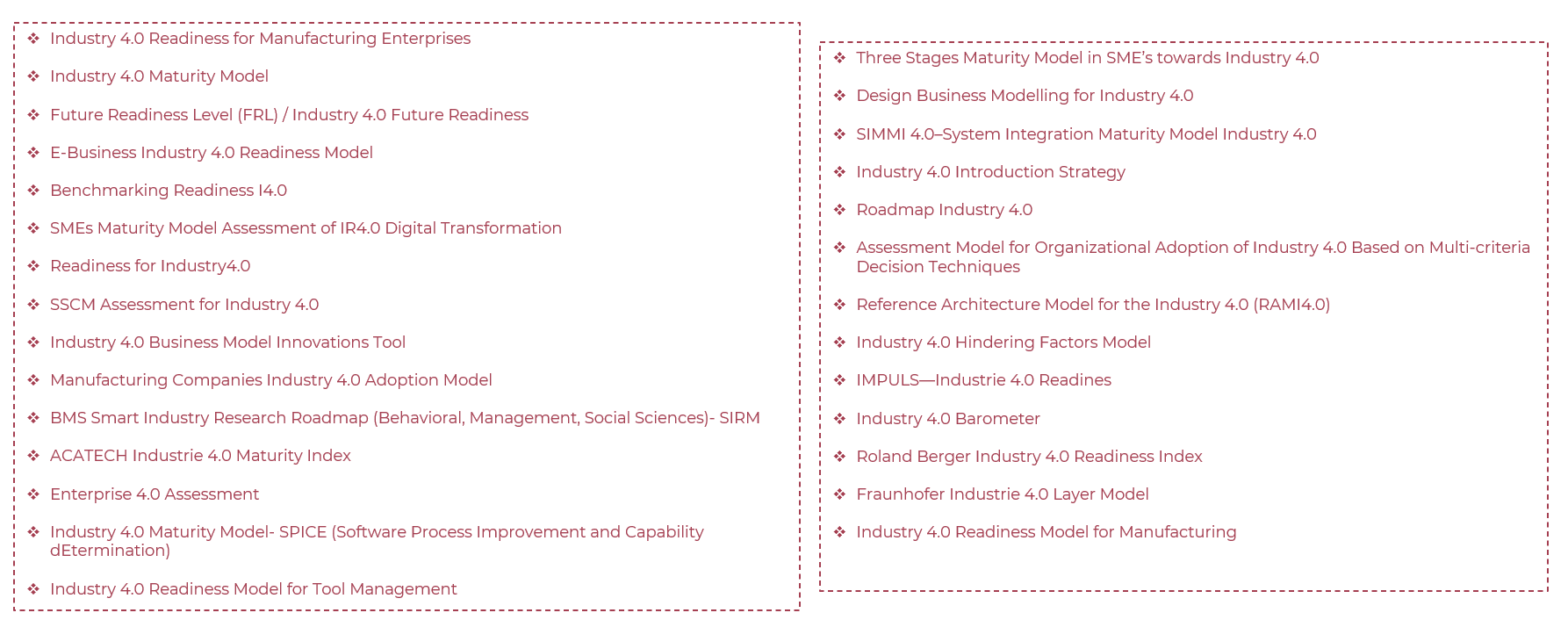
Readniess
Model Dimensions
Maturity Models